Understanding SWIFT CSP Compliance for Financial Institutions
By Rey LeClerc Sveinsson, PhD
The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) serves as the backbone for secure international financial transactions, connecting over 11,500 financial institutions globally.
In response to escalating cyber threats, SWIFT introduced the Customer Security Controls Framework (CSCF) to bolster the security of its network and ensure a unified defense against cyberattacks.
Understanding SWIFT CSP
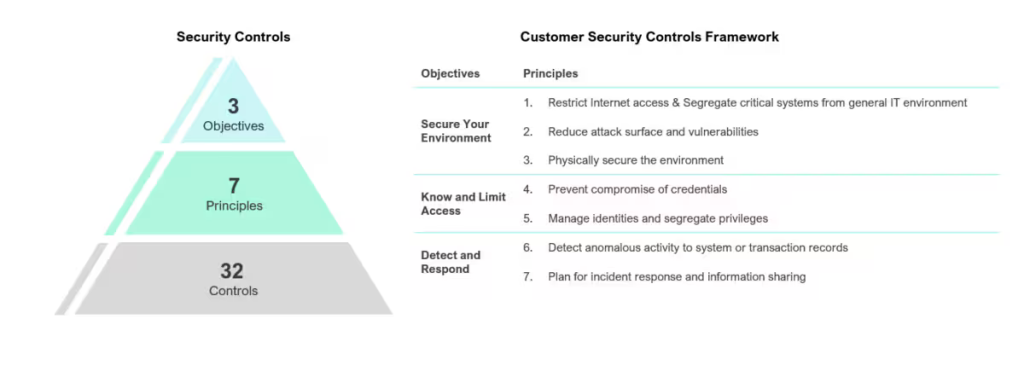
The CSCF comprises 32 security controls - 25 mandatory and 7 advisory - designed to safeguard financial institutions against cyber threats. Financial organizations must complete an Annual Attestation to demonstrate compliance, either by conducting self-assessments or engaging a third-party risk assessment company where compliance experts can independently validate compliance.
Many organizations choose risk assessment companies to conduct their SWIFT compliance assessment to foster transparency and trust within the financial ecosystem.
These third-party IT risk assessment services conduct IT security gap assessments to help organizations improve their security posture prior to a formal SWIFT risk assessment, leveraging expertise in the realms of both cybersecurity and data compliance.
The SWIFT controls are structured around three primary objectives.
- Secure Your Environment: Implement measures to restrict internet access, segregate critical systems, reduce vulnerabilities, and ensure physical security.
- Know and Limit Access: Prevent credential compromise by managing identities and segregating privileges effectively.
- Detect and Respond: Establish capabilities to detect anomalous activities and plan for incident response and information sharing.
Key Principles of SWIFT CSP
The seven foundational principles of the SWIFT Customer Security Program (CSP) offer a robust framework for safeguarding financial institutions against cyber threats. Here’s an expanded look at these principles, emphasizing their practical applications and strategic importance.
1. Restrict Internet Access and Segregate Critical Systems
Objective: Minimize exposure to external threats by limiting internet connectivity and isolating sensitive systems from potential attack vectors.
Controls to be implemented:
- Controlled Access: Use dedicated secure communication channels for systems accessing SWIFT services.
- Network Segmentation: Employ firewalls and Virtual LANs (VLANs) to segregate SWIFT infrastructure from other IT systems.
- Zero Trust Principles: Implement strict "need-to-know" policies and deny unnecessary access by default.
- Blocking Unapproved Traffic: Use network monitoring tools to flag unauthorized connection attempts.
2. Reduce Attack Surface and Vulnerabilities
Objective: Regularly update and secure systems to close off potential entry points for attackers.
Controls to be implemented:
- Vulnerability Management: Conduct routine vulnerability scans and apply patches promptly to address known weaknesses.
- Endpoint Security: Deploy anti-malware, intrusion detection, and prevention systems on all endpoints.
- Configuration Baselines: Maintain secure configurations for all SWIFT-connected systems and regularly audit them.
- Decommission Unused Services: Remove outdated software and disable unnecessary services to minimize the risk of exploitation.
3. Physically Secure the Environment
Objective: Prevent unauthorized physical access to critical infrastructure.
Controls to be implemented:
- Access Controls to be implemented: Use biometric systems, smart cards, or PINs to secure server rooms and data centers.
- Monitoring and Surveillance: Install CCTV cameras and retain footage for post-incident reviews.
- Visitor Management: Implement strict visitor sign-in protocols and escort policies in sensitive areas.
- Environmental Safeguards: Protect critical equipment against damage from environmental factors such as fire, flooding, or temperature fluctuations.
4. Prevent Compromise of Credentials
Objective: Strengthen the authentication mechanisms used to access systems and prevent unauthorized credential use.
Controls to be implemented:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require users to verify their identity through two or more authentication factors.
- Password Policies: Enforce strong password requirements, including complexity and periodic changes.
- Credential Encryption: Store credentials securely using hashing and encryption techniques.
- Phishing Awareness: Train employees to recognize and report phishing attempts targeting credential theft.
5. Manage Identities and Segregate Privileges
Objective: Assign the minimum necessary access rights and ensure appropriate segregation of roles.
Controls to be implemented:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Define roles and responsibilities with specific access rights aligned to operational needs.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic reviews of user privileges to ensure compliance with the principle of least privilege.
- Dynamic Privilege Management: Implement just-in-time (JIT) access systems to grant temporary elevated privileges when needed.
- Access Revocation: Ensure immediate deactivation of access rights for departing employees or when roles change.
6. Detect Anomalous Activity
Objective: Identify and respond to unusual behaviors within the SWIFT environment.
Controls to be implemented:
- Behavioral Analytics: Use machine learning models to establish baselines and detect deviations from normal behavior.
- Log Monitoring: Implement Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions to analyze logs in real time.
- Alerting Mechanisms: Configure alerts for critical events such as unauthorized access attempts, unusual transaction patterns, or system anomalies.
- Regular Drills: Conduct simulated cyberattacks to test detection capabilities and refine response processes.
7. Plan for Incident Response and Information Sharing
Objective: Prepare for and manage cybersecurity incidents while promoting transparency and collaboration.
Controls to be implemented:
- Incident Response Plans (IRP): Develop comprehensive IRPs with detailed workflows for various types of incidents.
- Crisis Management Teams: Establish dedicated teams trained to act swiftly in the event of a security breach.
- Periodic Testing: Regularly test the IRP through tabletop exercises and simulations.
- Information Sharing: Participate in industry forums and share threat intelligence with peers to stay ahead of emerging threats.
- Regulatory Reporting: Ensure compliance with local and international reporting requirements for data breaches and cyber incidents.
These seven principles not only enhance security but also align financial institutions with SWIFT's stringent compliance requirements. By implementing these strategies, institutions can protect their critical infrastructure, safeguard customer data, and maintain trust in the global financial ecosystem.
Engaging a third-party risk assessment company plays a critical role in achieving those goals.
Compliance Checklist for Financial Institutions
Achieving compliance with the SWIFT Customer Security Program (CSP) requires financial institutions to implement a structured approach that addresses key cybersecurity challenges. These steps are critical not only for meeting regulatory requirements but also for strengthening the overall security posture of institutions operating within the SWIFT ecosystem.
The foundation of SWIFT CSP compliance begins with Governance and Oversight. Financial institutions must establish a cybersecurity governance framework specifically tailored to SWIFT environments.
This involves assigning clear accountability to dedicated teams or individuals, such as a SWIFT security officer, and conducting periodic reviews of the framework to ensure it remains effective against evolving cyber threats. Developing detailed cybersecurity policies, engaging key stakeholders, and fostering a culture of security awareness are essential components of this process.
Securing the local environment is another cornerstone of compliance. This involves protecting endpoints by deploying robust anti-malware solutions, configuring firewalls, and regularly updating software to minimize vulnerabilities.
Physical security is equally important—financial institutions should restrict access to SWIFT infrastructure through biometric authentication, CCTV surveillance, and access logs. Environmental safeguards, such as temperature and humidity controls, should also be in place to protect critical systems from physical damage.
Effective Access Control is vital to preventing unauthorized access to sensitive systems. Role-based access controls (RBAC) should be enforced, ensuring users only have access to the resources they need.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) provides an additional layer of protection by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods. Institutions should also adopt Privileged Access Management (PAM) systems to monitor and secure privileged accounts and conduct regular audits to verify compliance with access policies.
Secure Messaging Practices ensure the confidentiality and integrity of financial messages transmitted over SWIFT. Advanced encryption protocols, such as TLS or AES, should be used to protect messages during transmission.
Digital signatures can authenticate messages and prevent tampering, while anomaly detection systems monitor messaging flows for irregular patterns that could indicate a breach. Additionally, secure archiving practices should be implemented to meet regulatory retention requirements.
Institutions must prioritize Monitoring and Threat Detection to detect and respond to potential threats promptly. Real-time monitoring tools, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, can analyze log data and identify unusual activities.
Advanced anomaly detection tools powered by artificial intelligence can establish baselines and highlight deviations. Regular vulnerability scans and penetration testing are essential for identifying weaknesses, and threat intelligence feeds can help institutions stay ahead of emerging risks.
A robust Incident Management strategy is critical for minimizing the impact of security incidents. Financial institutions should develop detailed incident response plans (IRPs) that outline roles, communication protocols, and response steps for various scenarios.
Crisis management teams should be trained to act swiftly during incidents, and regular drills or tabletop exercises should be conducted to test preparedness. Institutions must also adhere to SWIFT’s reporting timelines for disclosing incidents and equip teams with forensic tools to collect digital evidence when needed.
Regular Training and Awareness programs should educate employees about phishing, secure system usage, and compliance requirements. Phishing simulations can test employee readiness and improve their ability to identify malicious emails. Tailored training for specific roles and gamified learning methods can further enhance engagement and retention.
By following these steps, financial institutions can align with SWIFT CSP, mitigate risks, and ensure the security of their operations. This proactive approach not only meets regulatory standards but also contributes to the resilience and integrity of the global financial network.
ERMProtect Is A Risk Assessment Company for SWIFT CSP Compliance
ERMProtect is a leading cybersecurity firm specializing in helping financial institutions enhance their security posture and achieve compliance with industry regulations such as the SWIFT Customer Security Program (CSP).
Navigating the complexities of SWIFT CSP compliance can be challenging, but ERMProtect offers a comprehensive suite of services designed to guide organizations through each step of the risk assessment process.
One of the primary ways ERMProtect assists institutions is through comprehensive gap assessments. By evaluating an organization's current security controls against SWIFT's Customer Security Controls Framework (CSCF), ERMProtect identifies vulnerabilities and areas that require improvement. This thorough assessment provides actionable insights, allowing institutions to understand exactly what changes are needed to meet SWIFT's stringent security requirements.
Understanding that each financial institution has unique needs, ERMProtect develops tailored compliance roadmaps. These customized plans provide a step-by-step guide to achieving compliance, prioritizing critical controls and outlining clear timelines for implementation. This personalized approach ensures that organizations can address their specific challenges effectively and efficiently.
Implementing the necessary security controls is a critical aspect of SWIFT CSP compliance. ERMProtect's team of risk assessment experts assists in deploying both mandatory and advisory controls outlined in the framework. This includes establishing advanced access controls, configuring encryption protocols, setting up monitoring systems, and implementing other essential security measures to fortify SWIFT-related systems.
Should a security incident occur, ERMProtect provides specialized incident response and forensic investigations. The company’s digital forensic investigation team is ready to mitigate the impact of any breaches and assist in the recovery process.
With strong forensic capabilities, they help institutions investigate the root causes of incidents, enabling organizations to strengthen their defenses and prevent future occurrences.
Recognizing the importance of human factors in cybersecurity, ERM Protect also offers training and awareness programs. These programs educate employees on SWIFT CSP requirements, secure system usage, and how to recognize and respond to phishing attempts and other security threats.
By fostering a culture of security awareness, institutions can significantly reduce the risk of human error leading to security breaches.
To simplify the compliance process, ERMProtect assists with annual compliance validation and reporting. Their experts help institutions prepare for and complete the SWIFT annual attestation, ensuring accuracy and transparency in reporting. This service not only aids in meeting regulatory obligations but also fosters trust with counterparties and regulators by demonstrating a commitment to maintaining high security standards.
Why Choose ERMProtect As Your Risk Assessment Company?
Partnering with ERMProtect provides financial institutions with access to a team of seasoned cybersecurity professionals dedicated to delivering top-notch compliance solutions.
The company’s hands-on approach ensures that organizations do more than just meet SWIFT CSP requirements - they enhance their overall resilience against cyber threats. With ERMProtect's expertise, financial institutions can confidently secure their operations, protect sensitive customer data, and uphold the integrity of global financial transactions.
By leveraging ERMProtect's comprehensive risk assessment services, institutions navigate the complexities of SWIFT CSP compliance more effectively. This partnership ensures robust security measures are in place, contributing to a safer and more secure global financial ecosystem.
Learn more about our banking cybersecurity and compliance services here.
About the Author
Dr. Rey Leclerc Sveinsson is an expert in Privacy and Data Protection, Information Security, and Technology Governance, Risk & Compliance (IT GRC). He has developed information assurance programs for major organizations globally during his career as well as serving as a Consultant for ERMProtect. He has a PhD in Information Systems and multiple master’s degrees in the areas of privacy, information technology, and cybersecurity laws.
Subscribe to Our Weekly Newsletter

Turn your employees into a human firewall with our innovative Security Awareness Training.
Our e-learning modules take the boring out of security training.
Intelligence and Insights

Quantum Computing Puts Today’s Encryption at Risk

Are You Prepared for an AI-Powered Cyber Attack?