Implementing NIST Risk Assessments: A Step-by-Step Approach
By Rey LeClerc Sveinsson, PhD
Organizations must prioritize cybersecurity by adopting a robust NIST risk assessment framework. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides a comprehensive guideline for conducting IT risk assessments to enhance security postures.
By systematically implementing NIST risk assessments, businesses can proactively identify vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, and achieve regulatory compliance.
For CISOs and security leaders, the challenge is execution:
- How can assessments be streamlined?
- What tools and automation solutions can enhance efficiency?
- And how can organizations integrate risk assessments into existing security workflows?
This step-by-step guide will help organizations navigate the NIST risk assessment process effectively, leveraging the expertise of risk assessment companies and cybersecurity consulting services.
Step 1: Define the Scope of Your NIST Risk Assessment
Before diving into risk assessments, defining the scope is critical. This isn’t just about listing assets; it’s about making strategic decisions to ensure an efficient, high-impact assessment.
Before conducting a NIST risk assessment, organizations should define its scope, identifying the assets, systems, and networks that need evaluation. This includes determining whether the assessment will cover cyber security risk assessments related to FACTA, HIPAA, GLBA or FFIEC risk assessments.
A well-defined scope ensures that the assessment covers all potential risks while aligning with the organization’s business objectives and regulatory obligations. Organizations should first identify the specific areas requiring assessment, such as data storage infrastructure, cloud environments, internal networks, third-party integrations, or remote work security.
Defining the scope should also include understanding the potential compliance implications, ensuring that the assessment aligns with industry standards like PCI DSS certification for financial transactions or HIPAA risk assessment for healthcare data protection.
Additionally, organizations should engage key stakeholders, including IT, compliance, legal, and executive leadership, to establish a shared understanding of assessment objectives. This collaborative approach ensures that cyber security risk assessments address the most relevant threats and business priorities.
Risk assessment companies can provide guidance on regulatory frameworks, ensuring that assessments comply with industry standards and government regulations.
Another important aspect of defining the scope is determining the depth and breadth of the evaluation. Organizations may opt for a high-level assessment focusing on general security posture or a detailed technical assessment involving penetration testing services and vulnerability scans.
Red team penetration testing can simulate attack scenarios and provide valuable insights into system weaknesses. A comprehensive penetration testing report can further refine the scope by highlighting critical vulnerabilities.
Organizations should also define the timeline and resources required for the NIST risk assessment. This includes assigning internal teams or hiring external cybersecurity service providers to perform the assessment, analyze results, and recommend remediation strategies.
Additionally, incorporating incident response services and digital forensics investigators into the assessment plan can enhance an organization's readiness to handle security incidents such as credit card data breaches.
A properly scoped NIST risk assessment ensures that organizations can proactively manage security risks while achieving compliance with industry regulations.
By leveraging expert insights from risk assessment services, organizations can establish a strong security framework that protects sensitive data and maintains regulatory compliance.
Best Practices for Defining Scope Efficiently
- Map Critical Systems First: Rather than assessing every system at once, focus on the most business-critical assets. Prioritize based on risk exposure, regulatory requirements (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS, GLBA), and potential impact.
- Leverage Existing Frameworks: Many organizations already perform security audits, compliance checks, or vulnerability scans. Use these as a starting point rather than duplicating efforts.
- Use Asset Discovery Tools: Automated tools like Tenable, Qualys, or Rapid7 can help inventory IT assets and categorize them by risk profile, making scope definition faster and more accurate.
- Engage Key Stakeholders Early: Security teams, IT, compliance, and business units should be aligned on assessment objectives. Early collaboration prevents scope creep and ensures business priorities are reflected.
Efficiency Tip: If you have an annual compliance review cycle, align risk assessments with it. Conduct high-level reviews quarterly, with deep-dive assessments annually.
Step 2: Identify and Categorize Information Assets
Once the scope is defined, assets must be identified and categorized based on their sensitivity and regulatory obligations. The challenge? Many organizations lack a centralized, up-to-date asset inventory.
A successful IT security risk assessment begins with an inventory of critical assets. These assets include data repositories, IT infrastructure, applications, and communication channels. Organizations must classify these assets based on their sensitivity and regulatory requirements. For example, organizations handling payment card data must adhere to PCI DSS certification standards, necessitating PCI DSS penetration testing.
To effectively identify assets, organizations should map out all IT resources, including hardware, software, cloud environments, IoT devices, and databases. Understanding how these assets interact and where sensitive information is stored, transmitted, or processed is crucial for cyber security risk assessments.
Organizations should also assess whether assets are internally managed or externally hosted by third parties, as external dependencies introduce additional risk factors that require evaluation through IT risk assessment frameworks.
Once all assets are identified, organizations should classify them based on criticality, data sensitivity, and compliance requirements.
Common classifications include:
- Confidential Data: Includes financial records, personally identifiable information (PII), healthcare data (subject to HIPAA risk assessments), and payment card information (subject to PCI DSS certification).
- Business-Critical Systems: Includes enterprise applications, databases, and communication networks that, if disrupted, would significantly impact business operations.
- Public or Non-Critical Data: Includes information that, if exposed, would not pose a significant security or regulatory risk.
Asset categorization should also align with specific regulatory requirements. For example, GLBA risk assessments mandate the protection of consumer financial data, while FFIEC risk assessments ensure that financial institutions implement stringent security controls. Organizations handling personal credit data should also comply with FACTA risk assessments to protect against identity theft.
A thorough asset inventory and classification process form the foundation of an effective NIST risk assessment. By leveraging risk assessment services and cybersecurity consulting services, organizations can ensure that their most critical assets receive the appropriate level of protection and compliance oversight.
Implementation Tactics
- Deploy Automated Asset Management Solutions: Tools like Axonius, ServiceNow, and IBM QRadar help maintain an updated inventory of IT assets, reducing manual tracking.
- Classify Data by Impact:
- Confidential: PII, financial data, healthcare records (subject to HIPAA, PCI DSS).
- Business-Critical: Enterprise apps, cloud infrastructure, operational data.
- Public/Non-Critical: General information that, if exposed, has minimal impact.
- Tag Third-Party Dependencies: Identify assets that rely on third-party vendors. Risk assessments should include external dependencies (e.g., cloud providers, SaaS applications).
Efficiency Tip: Integrate classification into your data governance policies so that new assets are categorized at creation rather than during assessments.
Step 3: Identify Potential Threats and Vulnerabilities
A common issue with risk assessments is redundancy—identifying the same vulnerabilities year after year. Once assets are categorized, businesses should identify potential threats, such as cyberattacks, insider threats, and compliance risks.
Threats can stem from various sources, including external hackers, malicious insiders, or system vulnerabilities. Organizations should analyze past incidents, industry trends, and threat intelligence reports to recognize emerging risks.
Red team penetration testing can help simulate real-world attack scenarios, uncovering security weaknesses that traditional defenses may overlook. This proactive approach enables businesses to identify potential exploits before they are leveraged by malicious actors.
Penetration testing services provide insight into exploitable vulnerabilities, strengthening security controls and enhancing risk mitigation strategies.
A thorough penetration testing report details security flaws, prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their potential impact. Organizations should use these findings to implement remediation strategies, such as patching software, enhancing access controls, and fortifying network defenses.
Beyond technical threats, businesses should assess non-technical vulnerabilities, such as weak security policies, lack of employee awareness, and inadequate compliance adherence. Cybersecurity service providers can conduct IT security risk assessments to identify human factor risks and provide training programs to mitigate these threats.
Additionally, leveraging digital forensics services can help organizations investigate previous security incidents, gain insights into attack patterns and fortify defenses against future threats.
Working with digital forensics investigators ensures that security teams have access to forensic evidence, improving response efforts during a cyber security incident response or data breach response scenario.
A comprehensive threat and vulnerability assessment is essential for maintaining a strong security posture. By incorporating incident response services, penetration testing firms, and cybersecurity consulting services, businesses can proactively address risks and enhance their overall security resilience.
Optimized Approach
- Use Threat Intelligence Feeds: Services like Recorded Future or CrowdStrike Falcon X can enrich risk assessments with real-time threat intelligence.
- Conduct Continuous Security Testing:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Run automated scans regularly (e.g., Nessus, OpenVAS).
- Penetration Testing: Use red team exercises annually or post-major system changes.
- Breach and Attack Simulations: Platforms like SafeBreach or AttackIQ help validate security controls without waiting for real-world attacks.
Efficiency Tip: Schedule penetration tests strategically—align them with software updates, cloud migrations, or compliance audits to maximize value.
Step 4: Assess the Likelihood and Impact of Risks
Assessing risks isn’t about intuition; it’s about data. Organizations must evaluate the probability and potential impact of each identified risk. Cybersecurity service providers utilize both quantitative and qualitative methodologies to assess risks.
IT risk assessment frameworks such as NIST 800-30 help determine risk severity and prioritize mitigation strategies. Organizations should consider factors such as likelihood of exploitation, impact on business continuity, and regulatory repercussions.
A risk matrix approach, often used in IT security risk assessments, assigns a numerical value to threats, considering their frequency and severity. Partnering with risk assessment companies ensures accurate risk evaluations, enabling organizations to implement data-driven security strategies.
By continuously reassessing risks and refining security measures, businesses can enhance their resilience against evolving cyber threats.
How to Make This More Efficient
- Use a Risk Scoring System: Implement frameworks like FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk) alongside NIST guidelines for quantitative risk analysis.
- Automate Risk Analysis: Platforms like RiskLens or Archer can ingest security data and produce risk models automatically.
- Align with Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Collaborate with business continuity teams to integrate cyber risk into broader enterprise risk management.
Efficiency Tip: Instead of reviewing every risk in isolation, batch risks by category (e.g., all cloud risks, all endpoint risks) for more structured remediation planning.
Step 5: Implement Security Controls and Remediation Strategies
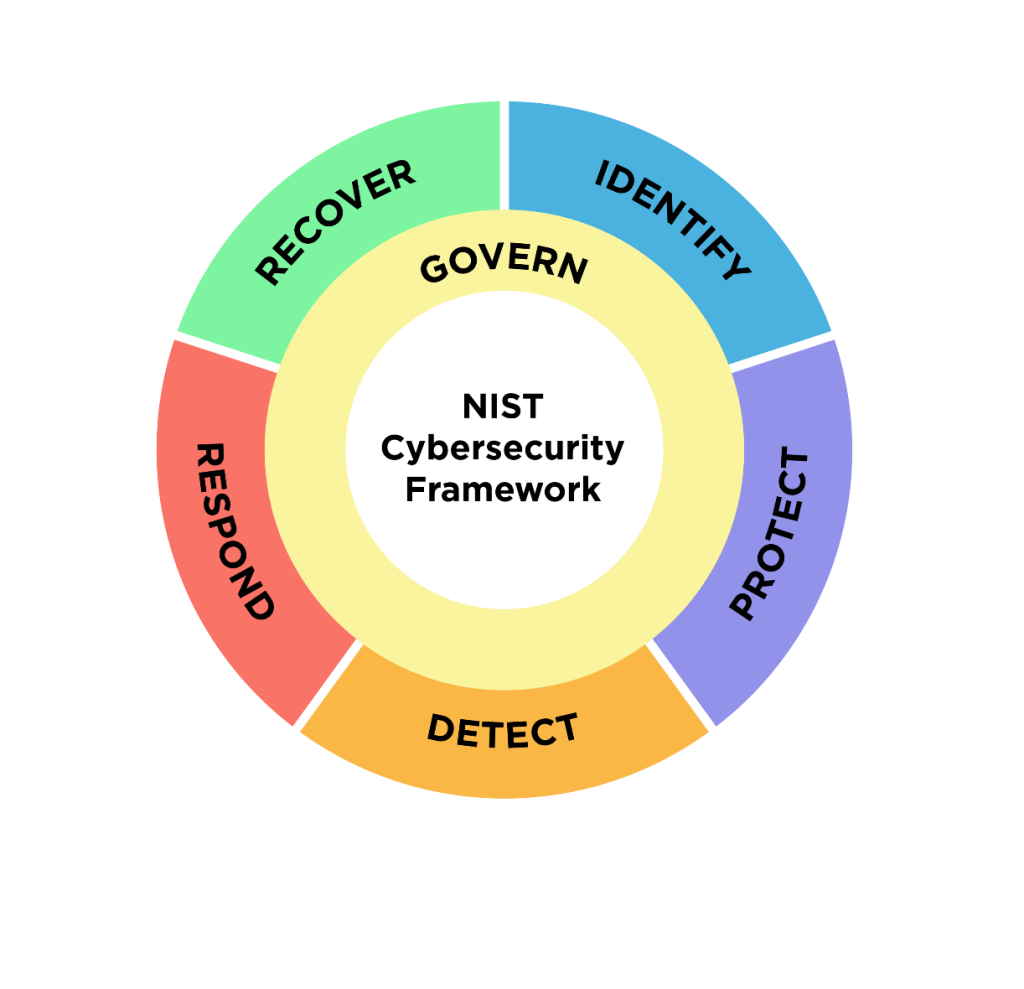
Implementation is where many risk assessments falter—organizations identify risks but struggle to act efficiently. Mitigation measures should align with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) and industry best practices.
Organizations must implement a layered security approach to mitigate risks effectively. This includes deploying penetration testing services, incident response services, and digital forensics services to address vulnerabilities in real time.
Key Security Controls to Implement
- Network Security Enhancements: Utilize firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and network segmentation to control traffic and reduce attack surfaces.
- Endpoint Security Measures: Deploy antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, and ensure timely patch management to safeguard devices.
- Access Control and Identity Management: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access controls (RBAC), and least-privilege principles to restrict unauthorized access.
- Data Protection and Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit using strong encryption protocols to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Regular Vulnerability Scanning and Patch Management: Red team penetration testing and continuous vulnerability scanning to detect and remediate security weaknesses.
- Security Awareness Training: Conduct regular cybersecurity training for employees to mitigate risks related to phishing attacks, social engineering, and insider threats.
- Incident Response Planning and Testing: Establish a well-documented incident response plan and conduct regular table-top exercises.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Implement compliance and regulatory requirements. For example, measures to protect against credit card breaches and maintain PCI DSS certification.
Remediation Strategies
- Immediate Threat Mitigation: Deploy emergency patches, disable compromised accounts, and isolate infected systems to prevent further damage.
- Long-Term Risk Reduction: Regularly review and update security policies, automate compliance checks, and integrate threat intelligence into security operations.
- Post-Breach Analysis: Utilize digital forensics investigators to analyze attack vectors, assess damage, and implement lessons learned into security strategies.
- Security Posture Improvements: Conduct regular penetration testing reports to assess improvements and refine security controls.
A well-structured NIST risk assessment must integrate these security controls and remediation strategies into daily operations.
By engaging cybersecurity service providers and risk assessment companies, businesses can create a resilient security framework that proactively defends against cyber threats.
How to Streamline Security Control Deployment
- Prioritize Based on Business Impact: Use the NIST CSF tiers to focus on high-risk areas first.
- Automate Security Policy Enforcement: Tools like Palo Alto Prisma, Microsoft Defender, or AWS Security Hub can enforce access controls, network segmentation, and compliance policies automatically.
- Embed Controls into CI/CD Pipelines: DevSecOps tools (e.g., Snyk, Checkmarx) help integrate security checks into software development workflows, reducing remediation costs later.
Efficiency Tip: Bundle security control rollouts with IT maintenance windows to minimize disruption.
Step 6: Conduct Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response Planning
Risk assessments shouldn’t be a once-a-year event; continuous monitoring is essential. Risk management is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and periodic cyber security risk assessments.
Establishing incident response services and engaging incident response companies ensures rapid detection and containment of security incidents. A proactive cyber security incident response strategy minimizes downtime and protects critical assets from further compromise.
Continuous Monitoring Strategies
- Real-Time Threat Detection: Implement Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to monitor network activity, detect anomalies, and alert security teams to potential threats.
- Automated Security Analytics: Utilize artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for behavioral analytics, helping to identify suspicious patterns and prevent breaches before they escalate.
- Regular Vulnerability Assessments: Perform routine IT security risk assessments and penetration testing services to identify weaknesses and ensure compliance with security frameworks like PCI DSS certification and HIPAA risk assessment.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Leverage global and industry-specific threat intelligence feeds to stay ahead of emerging cyber threats.
- Endpoint and Network Monitoring: Deploy Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Network Detection and Response (NDR) tools to identify malicious activity at multiple layers.
- Continuous Logging and Audit Trails: Maintain detailed logs for forensic analysis, compliance audits, and incident investigations.
Incident Response Planning and Execution
A well-defined incident response plan is critical for minimizing the impact of cyber threats. This plan should outline roles and responsibilities, escalation procedures, and remediation workflows to ensure a swift and effective response to security incidents.
- Preparation Phase: Establish an incident response team (IRT) composed of IT, security, legal, and executive stakeholders. Develop and test incident response playbooks for different attack scenarios, including ransomware, insider threats, and credit card data breaches. Conduct regular tabletop exercises to evaluate response readiness and identify gaps.
- Detection and Analysis: Utilize penetration testing reports and security monitoring tools to identify and analyze threats. Collaborate with digital forensics investigators to determine the root cause of security incidents and assess damage. Leverage cybersecurity consulting services to analyze potential compliance violations and legal implications.
- Containment and Eradication: Implement immediate containment measures, such as network isolation, access restrictions, and endpoint remediation. Deploy emergency patches and security updates to prevent further exploitation of vulnerabilities. Use incident response services from cybersecurity service providers to eliminate persistent threats.
- Recovery and Post-Incident Review: Restore affected systems and validate data integrity before resuming normal operations. Conduct a thorough digital forensics analysis to gather evidence, document findings, and enhance security controls. Perform a post-mortem analysis to strengthen defenses against future attacks and refine PCI compliance solutions and security frameworks.
By integrating continuous monitoring strategies and a structured incident response plan, organizations can enhance their resilience against cyber threats.
Collaborating with risk assessment companies, penetration testing firms, and digital forensics companies ensures a well-rounded approach to cybersecurity, ultimately reducing the risk of credit card breaches, data breach failures, and regulatory non-compliance.
Key Strategies
- SIEM + SOAR Integration: Combine SIEM (e.g., Splunk, LogRhythm) with SOAR (e.g., Cortex XSOAR, Swimlane) for automated incident detection and response.
- Threat Hunting: Use MITRE ATT&CK-based frameworks to proactively detect anomalies before they escalate.
- Automate Incident Workflows: Platforms like ServiceNow Security Operations can streamline alert triage and response.
Efficiency Tip: Conduct tabletop exercises quarterly and full incident response drills annually to keep teams prepared.
Step 7: Perform Regular Compliance Audits and Testing
Regulatory audits don’t have to be a burden if properly structured. To maintain compliance with regulatory frameworks like HIPAA, GLBA, FFIEC, and PCI DSS certification, organizations must conduct periodic audits.
PCI compliance certification audits ensure adherence to industry standards. Engaging a pen testing firm for penetration testing services supports ongoing security validation efforts.
Key Components of Compliance Audits and Testing
- Regulatory Compliance Audits: Organizations should conduct scheduled audits to ensure compliance with frameworks such as HIPAA, GLBA, and FFIEC risk assessments. These audits verify that security controls align with mandated regulatory requirements and help avoid legal penalties.
- Third-Party Security Assessments: Many organizations rely on external vendors, making third-party risk assessments essential. Risk assessment services can help evaluate vendors' compliance with cybersecurity regulations, ensuring they meet industry standards.
- PCI DSS Compliance Testing: Businesses that handle payment card transactions must regularly undergo PCI DSS certification audits. PCI compliance companies conduct these assessments to ensure proper handling and storage of credit card data, reducing the risk of credit card breaches.
- Penetration Testing and Security Validation: Engaging a pen testing firm for red team penetration testing helps identify vulnerabilities before cybercriminals can exploit them. Regular penetration testing reports provide valuable insights into security weaknesses and remediation measures.
- Internal Security Audits: Conducting in-house security audits helps organizations proactively assess IT security posture. These audits involve reviewing security policies, access controls, and data protection mechanisms to ensure compliance with IT security risk assessments.
- Automated Compliance Monitoring: Implementing compliance management solutions ensures continuous tracking of regulatory obligations. Automated tools monitor policy deviations, making compliance easier to maintain over time.
- Incident Readiness Reviews: Incident response services and digital forensics companies should be involved in routine compliance testing to assess how well an organization can respond to security incidents. These reviews help refine cyber security incident response protocols.
Benefits of Regular Compliance Audits and Testing
- Improved Security Posture: Routine audits and testing enhance overall cybersecurity defenses by identifying and mitigating risks proactively.
- Regulatory Adherence: Ensures that organizations remain compliant with legal and industry-specific requirements, reducing the risk of fines and penalties.
- Enhanced Customer Trust: Compliance with industry standards like PCI DSS certification and HIPAA risk assessment reassures customers that their data is handled securely.
- Reduced Data Breach Risks: Regular penetration testing services and compliance audits help prevent credit card data breaches and other security incidents.
- Streamlined Incident Response: By continuously validating security measures, organizations can improve their cybersecurity incident response efficiency.
By prioritizing regular compliance audits and testing, businesses can fortify their cybersecurity frameworks while maintaining regulatory compliance.
How to Simplify Compliance Audits
- Use Compliance Automation Tools: Solutions like Drata, Vanta, or Tugboat Logic help track controls, generate audit reports, and simplify evidence collection.
- Adopt Continuous Compliance Monitoring: Automate checks for policy violations and misconfigurations instead of waiting for annual audits.
- Outsource When Needed: If internal resources are stretched, leverage external PCI QSA firms or third-party security assessors.
Efficiency Tip: Map compliance controls across frameworks (NIST, ISO 27001, SOC 2) to avoid redundant efforts.
Step 8: Leverage External Expertise and Cybersecurity Consulting Services
Organizations can benefit from cybersecurity consulting services offered by cybersecurity service providers. These experts specialize in NIST risk assessments, IT security risk assessments, and digital forensics services. Working with digital forensics companies helps businesses conduct investigations and ensure regulatory compliance.
Key Benefits of External Cybersecurity Expertise
- Expert Guidance on Risk Assessments: Cybersecurity consultants bring deep expertise in NIST risk assessments, FACTA risk assessments, and IT security risk assessments, ensuring that organizations properly evaluate and mitigate risks.
- Access to Advanced Penetration Testing Services: Red team penetration testing, PCI DSS penetration testing, and other ethical hacking services to uncover security vulnerabilities.
- Regulatory Compliance Support: Cybersecurity service providers assist businesses in meeting regulatory requirements such as HIPAA risk assessment, GLBA risk assessment, and FFIEC risk assessment, helping them maintain compliance and avoid penalties.
- Incident Response and Digital Forensics: Incident response services from specialized firms provide immediate support in case of a security breach, while digital forensics investigators help analyze security incidents and recover compromised data.
- Customized Security Solutions: External experts offer tailored solutions for PCI compliance certification, PCI DSS certification, and data breach response, ensuring businesses implement security controls that fit their operational needs.
- Continuous Security Monitoring and Threat Intelligence: Engaging cybersecurity consulting services helps organizations stay ahead of cyber threats by implementing threat intelligence platforms, security analytics, and real-time monitoring tools.
- Third-Party Vendor Security Assessments: Many organizations rely on external vendors, making third-party risk assessments critical. Risk assessment companies conduct independent evaluations to ensure vendors comply with security policies and industry standards.
How to Choose the Right Cybersecurity Company
- Industry Experience: Look for providers with expertise in your industry and a track record of conducting IT security risk assessments, PCI DSS certification, and cyber security risk assessments.
- Comprehensive Services: Ensure the provider offers a full range of services, including penetration testing services, digital forensics services, and incident response services.
- Regulatory Compliance Expertise: Select a provider that specializes in relevant compliance requirements, such as HIPAA risk assessments, GLBA compliance, and PCI compliance solutions.
- 24/7 Support and Incident Response: Cyber threats can arise at any time; choose a cybersecurity service provider that offers round-the-clock monitoring and rapid incident response services.
- Proven Methodologies and Certifications: Verify that the provider follows industry best practices such as NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) and holds certifications like PCI QSA and ISO 27001.
By leveraging the expertise of cybersecurity consulting services, businesses can enhance their security posture, proactively manage cyber risks, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Collaborating with risk assessment companies, penetration testing firms, and digital forensics investigators provides the necessary tools and insights to safeguard digital assets and prevent cyber threats.
NIST Risk Assessment Solutions
A well-structured NIST risk assessment is essential for strengthening cybersecurity defenses and achieving regulatory compliance. By following this step-by-step approach, organizations can mitigate cyber risks, improve incident response capabilities, and secure sensitive data.
Risk assessments should be an ongoing, integrated part of security operations, not a disconnected checklist item. By automating asset discovery, leveraging threat intelligence, and prioritizing remediation based on business risk, CISOs can turn risk assessments into a strategic advantage.
By bundling assessments logically throughout the year, penetration testing with software updates, compliance audits with regulatory deadlines, and security controls with IT maintenance cycle organizations can reduce effort while improving security outcomes.
Security isn’t just about identifying risks; it’s about managing them efficiently. With the right tools, automation, and strategic alignment, NIST risk assessments can evolve from a compliance necessity into a proactive security enabler.
ERMProtect’s NIST Risk Assessment Services
ERMProtect is a leading cybersecurity service provider that offers a comprehensive suite of solutions to help businesses strengthen their security posture, conduct NIST risk assessments, and maintain regulatory compliance. Our expertise spans IT security risk assessments, penetration testing services, incident response planning, and digital forensics investigations, ensuring organizations can effectively manage cyber risks and protect critical data.
With a focus on NIST risk assessments, ERMProtect helps businesses identify vulnerabilities, assess threats, and implement robust security controls that align with industry standards. Additionally, our compliance solutions cover various frameworks such as HIPAA, GLBA, and FFIEC risk assessments, helping businesses meet legal and regulatory requirements.
By partnering with ERMProtect, organizations gain access to cybersecurity consulting services, third-party risk assessments, and continuous security monitoring, helping them stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Our tailored approach to risk assessment services and compliance management equips businesses with the necessary tools to safeguard sensitive data, reduce financial risk, and maintain trust our customers and stakeholders.
About the Author
Dr. Rey Leclerc Sveinsson is an expert in Privacy and Data Protection, Information Security, and Technology Governance, Risk & Compliance (IT GRC). He has developed information assurance programs for major organizations globally during his career as well as serving as a Consultant for ERMProtect. He has a PhD in Information Systems and multiple master’s degrees in the areas of privacy, information technology, and cybersecurity laws.
Subscribe to Our Weekly Newsletter

Turn your employees into a human firewall with our innovative Security Awareness Training.
Our e-learning modules take the boring out of security training.
Intelligence and Insights

Are You Prepared for an AI-Powered Cyber Attack?

AI Privacy Risks