Complete Guide to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0
By Collin Connors, ERMProtect IT Security Consultant
- Introduction to NIST and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- Why Compliance Matters
- The Framework Core and Its Functions
- The Six Functions
- Steps to Achieve Compliance
- Wrapping Up NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Introduction to NIST and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
What is NIST?
NIST Overview
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a part of the U.S. Department of Commerce dedicated to promoting U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards, and technology. As part of its mission, NIST is responsible for creating cutting-edge standards to guide businesses using industry best practices.
What is NIST’s Role in Cybersecurity?
In recent years, NIST has actively created leading industry standards for cybersecurity through the Computer Security Resource Center (CSRC). The CSRC is responsible for developing cybersecurity guidelines for organizations of all sizes and industries.
The guidance they create provides a comprehensive set of best practices to manage and reduce cybersecurity risks. Specifically, the NIST SP800 series of standards provides detailed guidance on all aspects of cybersecurity with specific standards targeted to various industries and organization sizes.
Using their guidelines, the NIST CSRC created the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) to aid organizations of all sizes in understanding cybersecurity.
Starting at 33:45, Collin Connors discusses the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and how to comply.
What is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is a voluntary framework developed to guide organizations in improving their cybersecurity practices. The framework offers a risk-based approach to managing cybersecurity risks. The framework is designed for organizations of any cybersecurity maturity level to follow. From small startups with no cybersecurity controls to large enterprises or critical infrastructure, the CSF guides creating, maintaining, and improving cybersecurity practices.
How Did the NIST Cybersecurity Framework Evolve?
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework came into being as a result of an Executive Order issued by President Obama in February 2013, in response to escalating cyberattacks. The NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 was published in February 2024, following stakeholder feedback. Here is a complete timeline:
- February 2013 - Executive Order 13636: President Obama issues an executive order directing NIST to develop a voluntary framework for reducing cyber risks to critical infrastructure.
- February 2014 - NIST Cybersecurity Framework 1.0 Released: NIST publishes the first version of the Cybersecurity Framework, providing a structure for organizations to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risks.
- April 2015 - NIST Cybersecurity Framework 1.1 Draft: NIST releases a draft version of the updated framework for public comment, aiming to refine and improve the initial framework based on stakeholder feedback.
- April 2018 - NIST Cybersecurity Framework 1.1 Final: The finalized version 1.1 of the framework is released, incorporating updates and enhancements based on public comments and evolving cybersecurity practices. Key additions include supply chain risk management and enhanced authentication guidance.
- December 2018 - NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 Preparation Begins: NIST begins updating the framework to version 2.0, gathering input from various stakeholders to address new and emerging cybersecurity challenges.
- January 2020 - NIST Requests Information: NIST issues a Request for Information (RFI) to gather feedback and recommendations from industry, academia, and other stakeholders for developing version 2.0.
- February 2021 - NIST Publishes Concept Paper: NIST releases a concept paper outlining proposed changes and enhancements for the upcoming Cybersecurity Framework 2.0, inviting further public comment and engagement.
- September 2021 - Public Workshops and Meetings: NIST conducts a series of public workshops and meetings to discuss the proposed updates, gather additional feedback, and engage with stakeholders on the framework's evolution.
- January 2023 - NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 Draft: NIST releases the draft version of the Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 for public comment, highlighting significant updates and new features to address contemporary cybersecurity challenges.
- May 2023 - Public Comment Period Ends: The public comment period for the draft version 2.0 concludes, allowing NIST to review and incorporate feedback from various stakeholders.
- February 2024 - NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 Final: The final version 2.0 of the Cybersecurity Framework is published, providing updated guidance and best practices for managing cybersecurity risks in an evolving threat landscape.
What are the Key Objectives of the Cybersecurity Framework?
The NIST CSF is designed to provide a common language and systematic methodology for managing cybersecurity risk. Ultimately, the framework can be used to help organizations:
- Understand the types of cyber threats they face.
- Manage their systems and people in an organized fashion to protect against cyber threats.
- Reduce cyber risk within the organization.
Why Compliance Matters
Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Many industries are governed by specific cybersecurity laws and regulations, such as many state and local governments, critical infrastructure providers, and companies that work with governments.
Compliance ensures adherence to these legal standards, avoiding penalties and legal issues. Furthermore, some states are considering passing laws that shield businesses that comply with cybersecurity frameworks from liability.
Furthermore, following the NIST framework helps meet regulatory guidelines set by government bodies and industry regulators. Many regulations are designed around the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and compliance with the NIST Framework may assist organizations in complying with other industry-specific cybersecurity regulations.
Risk Management and NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Compliance with the NIST framework helps organizations identify, protect, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber threats. Following the framework helps organizations understand and catalog the cyber threats they face. By creating controls that comply with the CSF, organizations can significantly reduce their cyber risk.
The NIST Cybersecurity framework guides organizations in managing risks proactively, reducing the likelihood of cybersecurity incidents.
Protecting Sensitive Information
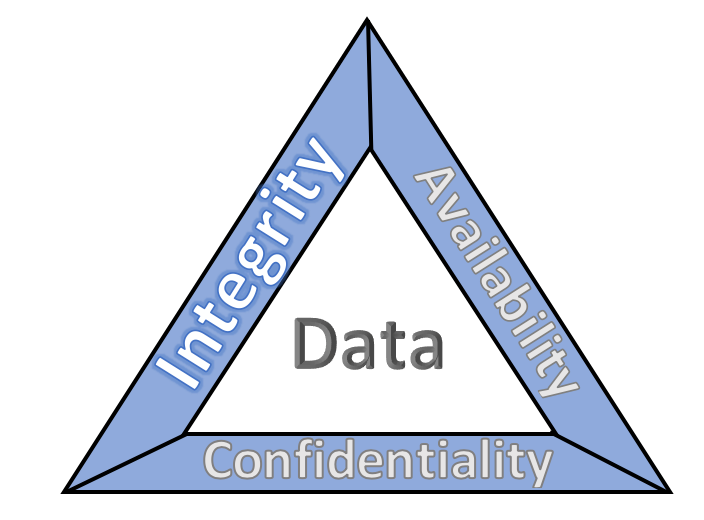
A central focus of the NIST CSF is Data Security. This means ensuring that organizations are managing data in a manner than protects:
- Confidentiality – Ensuring only authorized personnel can read the data.
- Integrity – Ensuring the data can only be modified or destroyed by authorized personnel.
- Availability – Ensuring that data is accessible to authorized personnel in a timely and reliable manner.
Complying with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework protects sensitive personal information, intellectual property, and financial data. Compliance can also prevent data breaches, leading to significant financial and reputational damage.
Enhancing Trust and Reputation
Demonstrating compliance builds trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders. A survey in 2022 by KPMG found that 1/3 of organizations recognized that trust leads to profitability. Still, nearly 2/3 of organizations reported complying with cybersecurity regulations because of compliance needs rather than long-term goals of increasing trust.
As data privacy and security concerns rise, organizations must show the public they are responsible for their data. Complying with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework can enhance an organization's reputation, making it a respected entity committed to cybersecurity.
Financial Implications
Data breaches negatively impact a company’s reputation and can incur a high financial cost. According to IBM’s data breach report, the average data breach cost 2023 was $4.45 million. This is a 15% increase over three years. Organizations lacking high-security skills faced a staggering average data breach cost of $5.36 million.
Organizations that were not compliant with regulations faced an average of $218,915 more in costs of data breaches than their counterparts who did comply with regulations. Furthermore, from the same report, 20% of organizations that experienced a data breach paid over $250,000 in fines.
Click here for a list of Top 10 Data Breaches in 2023
The Framework Core and Its Functions
Framework Core
Definition and Purpose
The core is a set of cybersecurity activities, desired outcomes, and applicable references common across sectors. The core provides a foundation for developing individual, organizational profiles. Because the NIST framework is designed to be used by organizations of any size or industry, it does not provide specific controls to follow. Still, it allows organizations to create custom sets of controls that best meet the applicable standards and regulations.
For example, rather than requiring organizations to encrypt all data in transit using at least TLS 1.2, the CSF prescribes that "the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data-in-transit are protected." Some organizations may take this to mean only allowing TLS1.2 with a strict list of allowed ciphers. In contrast, other organizations where the risk to data in transit has less impact on their business may be more lenient with the cipher suites permitted.
Components of the Core
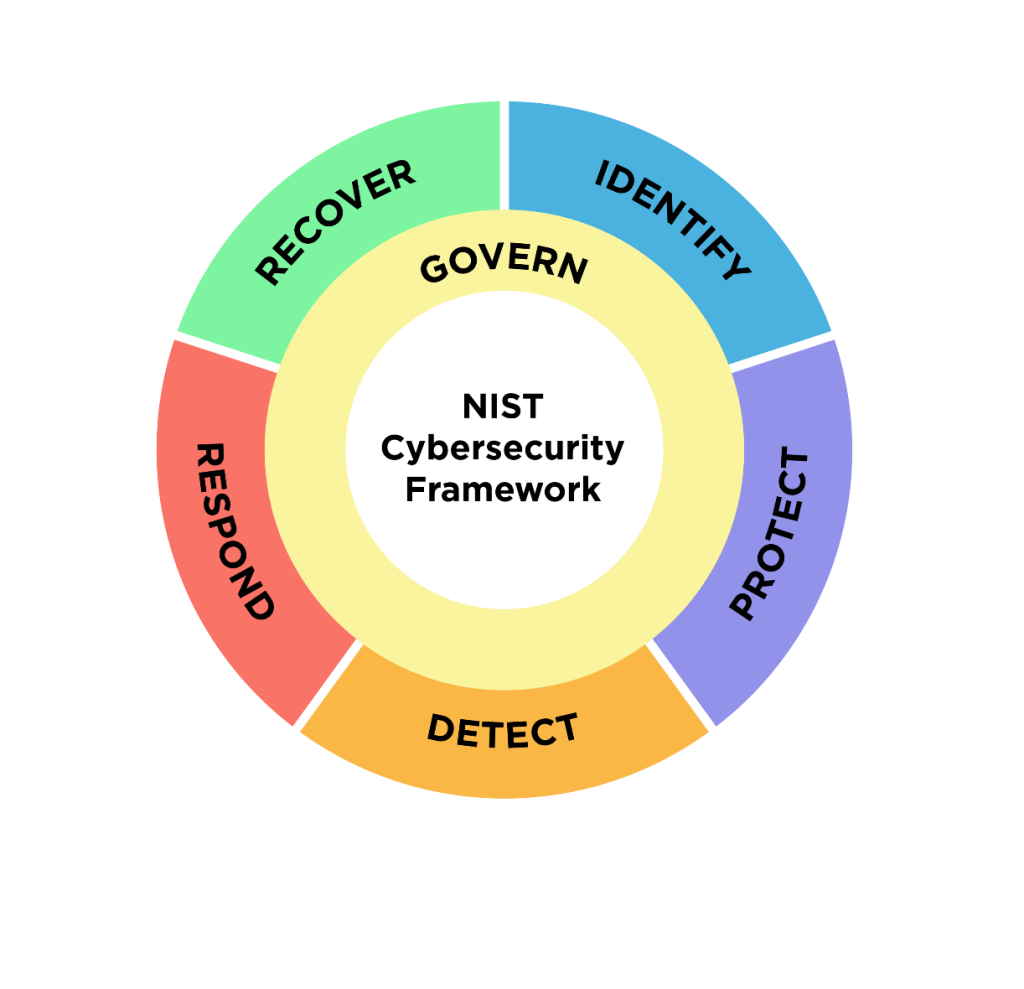
NIST CSF breaks managing and maintaining cybersecurity into Functions, Categories, and Subcategories. There are six top-level functions, each described as a top-level cybersecurity objective.
- GOVERN – establish and monitor cybersecurity risk management strategy, expectations, and policy.
- IDENTIFY - determine the current cybersecurity risk.
- PROTECT - use safeguards to prevent or reduce cybersecurity risks.
- DETECT - find and analyze possible cybersecurity attacks and compromises.
- RESPOND - take action regarding a detected cybersecurity incident.
- RECOVER - restore assets and operations that were impacted by a cybersecurity incident.
Each function contains several categories, which are mid-level goals that should be met to comply with the function. These categories each contain subcategories, low-level control categories that organizations should strive to fulfill. For example, the Identify function contains the category Asset Management, which includes subcategories focused on identifying all assets within an organization.
The Six Functions of NIST Cybersecurity Framework
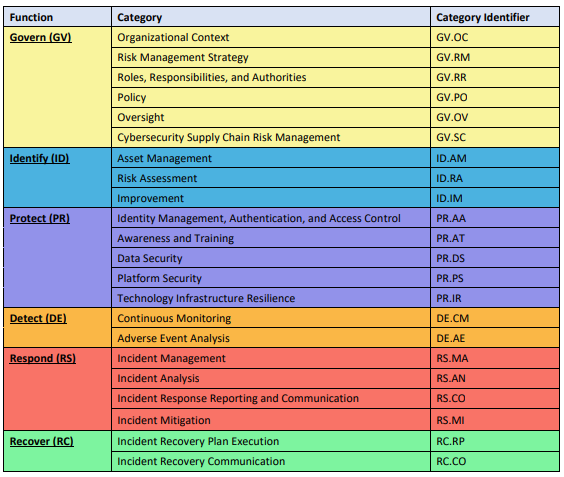
Figure 3: The six NIST Core Functions and their Categories (Table from NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0)
The NIST Govern Function
Purpose: Establish & Monitor Cybersecurity Risk Strategies across an organization
Summary: The Govern function provides the backbone of cybersecurity across the organization. This function helps organizations make cybersecurity part of the organization's DNA. The Govern function brings together members across the organization to ensure cybersecurity risks are communicated and enforced. Importantly, this function strives to ensure that cybersecurity is prioritized at the highest levels of an organization.
Categories:
- Organizational Context - Legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements related to cybersecurity risk management decisions are understood.
- Risk Management Strategy - Priorities, constraints, and risk tolerance appetites are established, communicated, and used to support operational risk decisions.
- Roles, Responsibilities, and Authorities - Cybersecurity roles, responsibilities, and authorities are established and communicated to foster accountability, performance assessment, and continuous improvement.
- Policy - Cybersecurity policy is established, communicated, and enforced.
- Oversight - Cybersecurity risk management activity results and performance are used to inform, improve, and adjust the risk management strategy.
- Cybersecurity Supply Chain Risk Management - Supply chain cyber risk management processes are identified, established, managed, monitored, and improved.
The NIST Identify Function
Purpose: Determine Current Cybersecurity Risk
Summary: The identify function contains controls related to determining an organization's cyber risk. First, an organization must understand what assets they need to protect. This includes software and hardware but extends to the organization's systems, physical locations, services, and people. Furthermore, organizations need to understand the risks their third-party vendors pose. Through risk assessments, organizations can identify threats and prioritize implementing controls to mitigate them.
Categories:
- Asset Management - Assets (e.g., data, hardware, software, systems, facilities, services, people) are identified and managed consistently with relative importance to organizational objectives and risk strategy.
- Risk Assessment - The organization understands the cybersecurity risk to the organization, its assets, and individuals.
- Improvement - Improvements to cybersecurity risk management processes, procedures, and activities are identified across all CSF Functions
The NIST Protect Function
Purpose: Use Safeguards to Prevent or Reduce Cybersecurity Risks
Summary: The Protect function of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework is critically important because it encompasses the essential safeguards and controls needed to ensure the security and resilience of an organization's systems and data. This function involves implementing access control, awareness and training measures, data security, information protection processes and procedures, maintenance, and protective technology. Effective implementation of this function reduces the risk of cybersecurity incidents, supporting business continuity and protecting the organization's reputation.
Categories:
- Identity Management, Authentication, and Access Control - Access to physical and logical assets is limited to authorized users, services, and hardware and managed commensurate with the assessed risk of unauthorized access.
- Awareness and Training - Personnel are provided with cybersecurity awareness and training.
- Data Security - Data confidentiality, integrity, and availability are managed consistently with the organization's risk strategy.
- Platform Security - The hardware, software, and services of physical and virtual platforms are managed in a manner consistent with the organization's risk strategy to protect their confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Technology Infrastructure Resilience - Security architectures are managed to protect asset confidentiality, integrity, availability, and organizational resilience.
The NIST Detect Function
Purpose: Find & Analyze Possible Compromises
Summary: The Detect function focuses on the timely identification of cybersecurity events, enabling organizations to respond swiftly and mitigate potential damage. This function involves implementing continuous monitoring systems, establishing detection processes, and analyzing anomalies and security events. By promptly identifying cybersecurity incidents, organizations can limit their impact, prevent the escalation of attacks, and safeguard sensitive data and systems.
Categories:
- Continuous Monitoring - Assets are monitored to find anomalies, indicators of compromise, and other potentially adverse events.
- Adverse Event Analysis - Anomalies, indicators of compromise, and other potentially adverse events are analyzed to characterize the events and detect cybersecurity incidents.
The NIST Respond Function
Purpose: Take Action Regarding a Detected Incident
Summary: The Response function outlines the necessary actions to be taken once a cybersecurity event is detected, enabling organizations to manage and mitigate the impact of such incidents effectively. Key activities within the Respond function include developing and maintaining an incident response plan, establishing clear communication channels, analyzing incidents to understand their scope and impact, taking steps to contain and eradicate the threat, and learning from the incident to improve future responses.
Categories:
- Management - Responses to incidents are managed.
- Analysis - Investigations are conducted to ensure effective response and support forensics and recovery activities.
- Reporting and Communication - Response activities are coordinated with internal and external stakeholders as laws, regulations, or policies require.
- Mitigation - Activities are performed to prevent the expansion of an event and mitigate its effects.
The NIST Recover Function
Purpose: Restore Assets & Operations
Categories:
- Incident Recovery Plan Execution - Perform restoration activities to ensure operational availability of systems and services affected by cybersecurity incidents.
- Incident Recovery Communication - Coordinate restoration activities with internal and external parties.
Summary: The Recover function focuses on restoring and recovering services and capabilities that were impaired due to a cybersecurity incident. This function includes developing and implementing recovery plans, improving recovery strategies, and communicating effectively during and after recovery efforts. Key activities within the Recover function involve identifying lessons learned, updating recovery plans based on past experiences, and conducting regular tests and drills to ensure preparedness.
Steps to Achieve Compliance
Step 1: Gap Analysis
Performing a gap analysis is the first step for organizations aiming to achieve compliance with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
This process involves systematically comparing the current state of the organization's cybersecurity practices against the standards and best practices outlined in the framework. The analysis identifies areas where the organization meets the requirements and highlights gaps where improvements are necessary.
By thoroughly assessing existing policies, procedures, and controls, organizations can pinpoint specific weaknesses and vulnerabilities that need to be addressed. The gap analysis results provide a clear roadmap for enhancing cybersecurity measures, prioritizing actions based on risk levels, and allocating resources effectively. Following the gap analysis, organizations can begin to remediate any exceptions noted methodically to ensure they are ready for compliance.
Step 2: NIST Cybersecurity Framework Audit
After the exceptions have been mitigated, the organization will be ready for a full NIST Cybersecurity Framework Audit.
This involves a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s cybersecurity practices, ensuring that all policies and procedures are followed, and recommending improvements to level up an organization’s cybersecurity maturity. This audit ensures that the organization aligns with best practices and effectively manages and mitigates cybersecurity risks. A full audit should be performed annually.
How Do I Comply with the NIST Identify Function?
Organizations should perform annual security configuration reviews. This is the process of checking the security settings for any software or hardware the organization uses. For example, the VPN rules should be reviewed during this process. At one point, the organization may have opened VPN access to a third party but never closed that third party's access at the end of the engagement.
Annual risk assessments help organizations identify the current threats faced. To perform a risk assessment organization, one must understand what assets they are trying to protect. Then, the organization must identify the threats these assets face and the probability of the threat occurring. Finally, organizations should determine what controls are in place to mitigate that threat.
For example, an organization might be concerned about its web server being encrypted with ransomware. They would perform an impact analysis to determine the probability and impact of that server being encrypted. Then, the organization would look for mitigating controls, such as backing up the server to allow offline backups.
How Do I Comply with the NIST Protect Function?
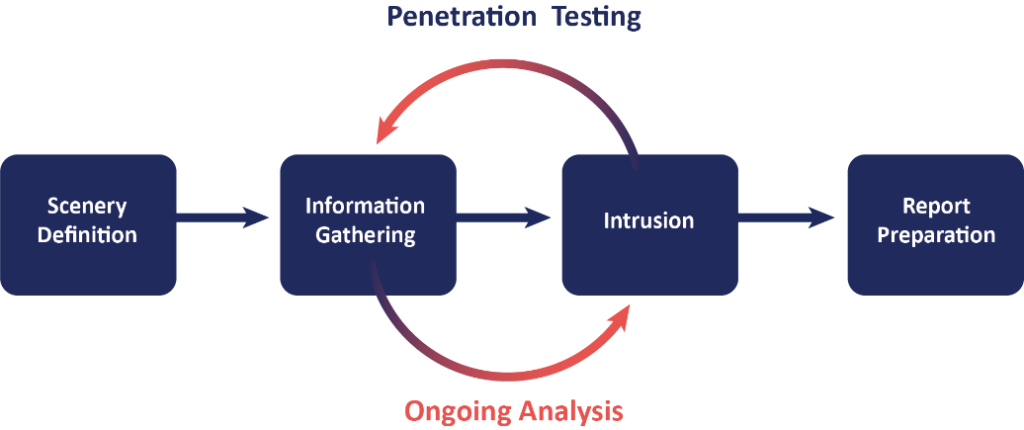
Penetration testing (pen-testing) is essential for identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. By simulating real-world attacks, pentesting reveals weaknesses in systems, networks, and applications, allowing organizations to implement effective countermeasures. Regular pen testing enhances security defenses, ensures compliance with industry standards, and demonstrates a commitment to maintaining a secure environment. In an era of sophisticated cyber threats, pentesting is crucial for protecting sensitive data, maintaining business continuity, and safeguarding an organization's reputation.
An organization may have a highly skilled technical team and implement top-tier technologies. However, attackers can still get in by targeting humans. Security awareness training is vital for equipping employees with the knowledge and skills to recognize and respond to cybersecurity threats. By educating staff on best practices, such as identifying phishing attempts, using strong passwords, and handling sensitive information securely, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of human error, leading to security breaches.
Following security awareness training, testing employees for phishing exercises is important. These simulated phishing attacks expose employees to the techniques used by real-world hackers to ensure they are prepared. These attacks further solidify the knowledge learned in security awareness training by allowing employees to practice what they were taught.
How Do I Comply with the NIST Detect Function?
Red team assessments are crucial for evaluating an organization's security defenses through simulated attacks that mimic real-world threat scenarios. By employing adversaries' tactics, techniques, and procedures, red team exercises reveal vulnerabilities and gaps in security measures that traditional testing might miss. These assessments provide valuable insights into how well an organization can detect, respond to, and mitigate advanced threats. The findings from red team activities help organizations strengthen their defenses, improve incident response strategies, and enhance overall resilience against cyber-attacks, ultimately ensuring a more robust security posture.
How Do I Comply with the NIST Respond Function?
A tabletop exercise is a discussion-based simulation where team members gather to walk through a hypothetical cybersecurity incident in a structured manner. This exercise is crucial as it allows participants to evaluate and improve their response plans and coordination in a low-stress environment. A tabletop exercise ensures that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities during an incident by involving members from across the organization, including IT, legal, communications, and executive teams. This collaborative approach helps identify potential gaps in the response plan, enhances communication and decision-making processes, and ultimately strengthens the organization's preparedness for real-world cyber threats.
How Do I Comply with the NIST Compliance Function?
Digital forensics is critical following a data breach, as it involves systematically collecting, analyzing, and preserving electronic evidence to understand the extent and impact of the breach. This process helps identify how the breach occurred, what data was compromised, and who was responsible. The insights gained from digital forensics enable organizations to remediate vulnerabilities, improve security measures, and prevent future incidents. Additionally, thorough forensic investigations are essential for regulatory compliance, legal proceedings, and maintaining the trust of customers and stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to addressing and resolving the breach effectively.
Wrapping Up NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Importance of the NIST Framework
Understanding and implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework is crucial for managing cybersecurity risks. The framework is designed so organizations of all sizes can benefit from it.
Complying with the framework can reduce the cyber risk that organizations face, leading to lower financial costs, a better reputation, and less friction with regulators. Organizations should ensure compliance with the six functions: govern, identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover, to minimize cybersecurity risk.
How ERMProtect Can Help With NIST Cybersecurity Framework
ERMProtect offers a variety of services for ensuring compliance with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework as well as other cybersecurity standards, including:
- NIST Gap Analysis
- NIST Framework Audit
- Policy and Procedure Review, Refinement, and Design
- Security Configuration Audit
- NIST Risk Assessment
- Internal Penetration Testing
- External Penetration Testing
- Web Application Penetration Testing
- Wireless Network Penetration Testing
- Security Awareness Training
- Phishing Assessment
- Red Team Assessments
- Tabletop Exercises
- Digital Forensics
- For a full list of services, refer to our service guide
In business for 26 years, we have served more than 500+clients across 39+ industries giving us deep insight into vulnerabilities that lead to data breaches. For more information, please email Judy Miller at [email protected] or call 305-447-6750.
About the Author
Collin Connors is a Senior Information Security Consultant at ERMProtect Cybersecurity Solutions in Coral Gables. He leads engagements related to penetration testing, social engineering, IT risk assessments, digital forensics, and cryptocurrency fraud. He has undergraduate degrees in Mathematics and Computer Science and is a fourth-year Ph.D. candidate at the University of Miami, researching AI applications, blockchain, and cybersecurity.
Subscribe to Our Weekly Newsletter
Intelligence and Insights

Aligning Your Incident Response Plan with NIST SP 800-61 Rev. 3

CEO Checklist: How To Know If Your Organization Is Cyber Secure