Top 10 Emerging Cyber Trends in 2025
By Rey LeClerc Sveinsson, PhD
As we navigate through 2025, the digital landscape continues to evolve, bringing both advancements and challenges in cybersecurity. Understanding the emerging trends in this field is crucial for individuals and organizations to protect their digital assets effectively.
Here are our recommendations for organizations in 2025 based on these cyber trends:
1. Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM): Staying Ahead of Cyber Threats
In an era where cyber threats evolve rapidly, traditional cybersecurity methods that rely periodic assessments are no longer sufficient. These outdated approaches often leave significant time gaps between evaluations, during which vulnerabilities may go unnoticed and unaddressed, providing cybercriminals with opportunities to exploit weaknesses. Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is a modern, proactive strategy designed to tackle this issue head-on by providing organizations with an ongoing, dynamic assessment of their cybersecurity landscape.
CTEM works by continuously monitoring an organization's digital ecosystem to identify vulnerabilities in real time. This approach evaluates potential threats not just in theory but based on their real-world exploitability, allowing businesses to focus on the risks that pose the greatest danger.
By prioritizing vulnerabilities according to their likelihood and potential impact, CTEM enables organizations to allocate their resources more effectively, addressing critical risks first rather than spreading efforts too thinly across less significant issues.
Moreover, CTEM fosters a culture of vigilance and preparedness within organizations. It shifts the focus from reactive damage control to proactive threat management, empowering businesses to stay one step ahead of adversaries. This method is particularly valuable in complex IT environments where new vulnerabilities can emerge as systems evolve or integrate with new technologies.
With CTEM, companies can maintain a continuous loop of risk identification, evaluation, and remediation, ensuring that their cybersecurity defenses remain robust and adaptive in an ever-changing threat landscape.
Ultimately, CTEM is not just a technological solution but a strategic approach that helps organizations build resilience against cyber threats. By adopting CTEM, businesses can safeguard their operations, protect sensitive data, and enhance their overall cybersecurity posture, gaining a crucial advantage in today’s digital world.
CTEM Preparation Tips
- Implement Continuous Monitoring: Adopt tools that provide real-time insights into your network's security posture, allowing for immediate detection and response to threats.
- Prioritize Vulnerabilities: Focus on vulnerabilities that pose the highest risk, rather than attempting to address all potential issues simultaneously.
- Foster a Proactive Security Culture: Encourage a mindset that anticipates threats and addresses them before they can be exploited.
2. Securing Active Directory (AD): Protecting Access Controls
Active Directory (AD) is the backbone of identity and access management for many organizations, playing a pivotal role in regulating who has access to specific systems, files, and applications. It serves as a central hub for managing user credentials, enforcing security policies, and assigning permissions.
Due to its integral role in maintaining operational efficiency and security, AD has become a prime target for cybercriminals. Attackers often seek to exploit misconfigurations, outdated credentials, or insufficient monitoring to gain unauthorized access, which can lead to severe breaches.
Securing AD is, therefore, a top priority for organizations aiming to protect sensitive data and maintain operational integrity. A breach of AD can grant attackers access to critical resources across an organization's network, potentially enabling them to escalate privileges, move laterally, and compromise multiple systems.
Given the potential risks, robust security measures are essential to safeguard AD and ensure its proper functioning.
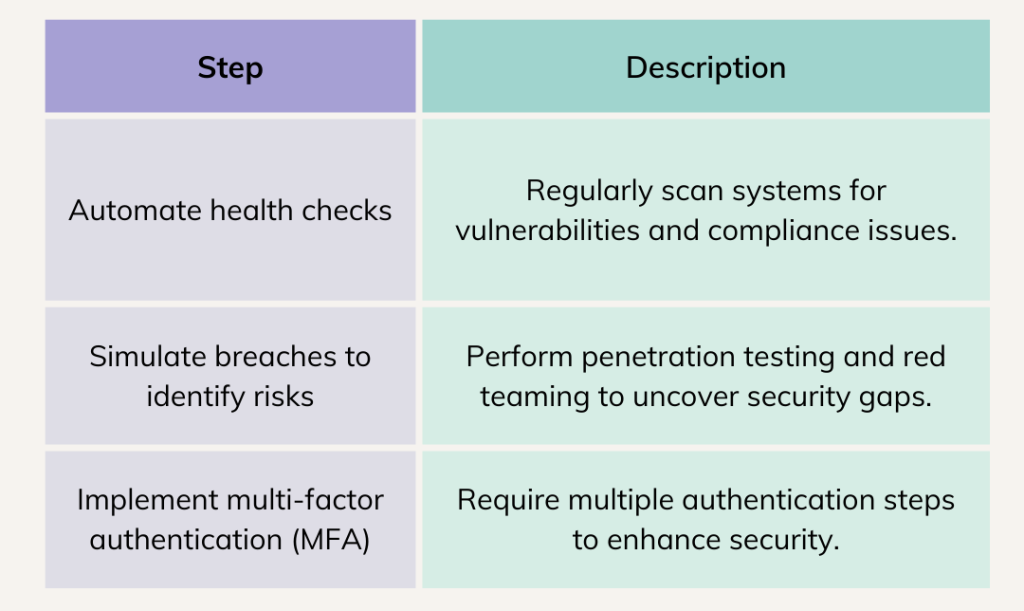
Effective AD security begins with regular health checks to identify and rectify vulnerabilities such as unused accounts, weak passwords, or misconfigured permissions. Organizations should automate these checks wherever possible to ensure continuous compliance with security best practices. Additionally, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for AD logins adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
Another critical step is to simulate potential breaches through penetration testing or red team exercises. These simulations help organizations identify weaknesses in their AD environment, enabling them to strengthen defenses proactively.
By continuously monitoring AD activity for unusual patterns or unauthorized changes, businesses can detect and respond to threats before they escalate.
Ultimately, securing Active Directory is not just about protecting user accounts; it’s about safeguarding the entire digital ecosystem.
A well-protected AD ensures that access controls are enforced effectively, minimizing the risk of breaches, and helping organizations maintain trust and stability in their operations.
Active Directory Preparation Tips
- Conduct Regular Health Checks: Perform routine assessments to identify and rectify misconfigurations or outdated accounts.
- Automate Security Audits: Utilize automated tools to continuously monitor AD for compliance with security best practices.
- Simulate Breaches: Regularly test your AD environment to understand potential exploitation paths and strengthen defenses accordingly.
3. Attack Graphs: Visualizing Potential Threat Pathways
In the complex world of cybersecurity, understanding how cybercriminals might exploit vulnerabilities is essential for effective defense. Attack graphs are a powerful tool that helps organizations visualize potential routes an attacker could take to infiltrate a system.
These graphs map out interconnected vulnerabilities, systems, and pathways, a clear and comprehensive picture of an organization’s security landscape. By illustrating how a potential breach could unfold, attack graphs enable businesses to anticipate and block attacks before they occur.
One of the key advantages of attack graphs is their ability to prioritize risks. Not all vulnerabilities are equally dangerous, and some are more likely to be exploited due to their accessibility or the critical systems they affect. Attack graphs highlight these high-risk points, allowing organizations to focus their resources on addressing the most pressing issues first. This targeted approach enhances efficiency and ensures that limited cybersecurity budgets are spent wisely.
Attack graphs also foster collaboration between technical teams and decision-makers by translating complex cybersecurity data into a format that is easier to understand. This shared understanding helps align efforts across the organization, ensuring that cybersecurity measures are well-integrated into broader business strategies.
Additionally, these visualizations are invaluable during audits or compliance assessments, as they provide tangible evidence of an organization's security posture.
Furthermore, attack graphs are not static tools. As new vulnerabilities emerge or systems are updated, the graphs can be dynamically adjusted to reflect the current state of the network. This adaptability ensures that organizations remain prepared for evolving threats, keeping their defenses robust and relevant.
By leveraging attack graphs, businesses can move from reactive to proactive cybersecurity practices. Instead of responding to breaches after they occur, organizations can preemptively identify and address vulnerabilities, significantly reducing the likelihood of successful attacks.
In an age where cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, attack graphs serve as an essential component of a resilient cybersecurity strategy.
Attack Graph Preparation Tips
- Leverage Attack Graph Technology: Use these tools to map out and understand the interconnected vulnerabilities within your network.
- Identify Critical Nodes: Determine which points in your network are most susceptible to attack and prioritize their security.
- Enhance Network Segmentation: Implement measures to isolate different parts of your network, limiting the spread of potential breaches.
4. Cloud Security: Safeguarding Data in the Digital Sky
The adoption of cloud services has revolutionized the way organizations store, manage, and access data. Cloud platforms offer unmatched flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency, allowing businesses to innovate and operate with greater agility. However, this shift to the cloud also brings unique security challenges that organizations must address to protect their sensitive data and maintain trust.
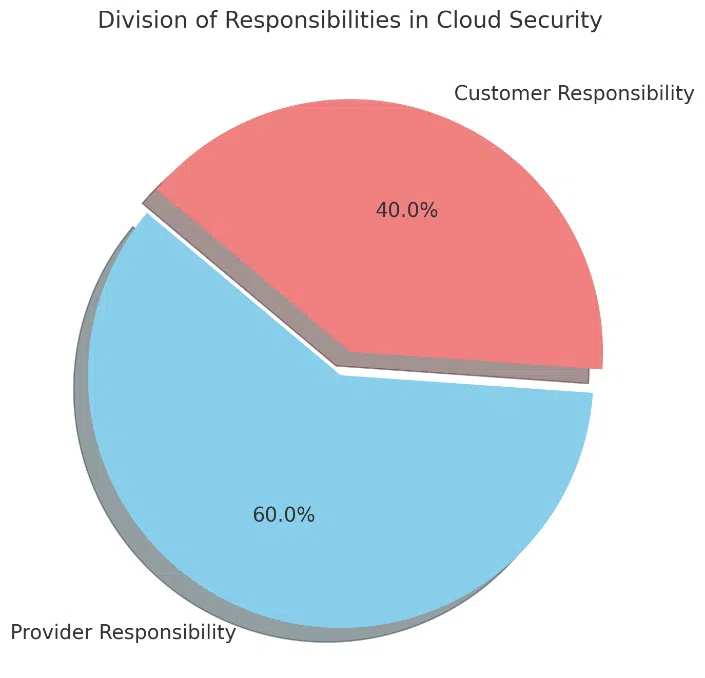
One of the primary challenges of cloud security is the shared responsibility model. In this framework, the cloud provider is responsible for securing the infrastructure, while the customer is accountable for safeguarding their data and managing user access. Misunderstandings about these roles can lead to security gaps, leaving companies vulnerable to breaches. Organizations must clearly understand their responsibilities and implement appropriate safeguards to fulfill them.
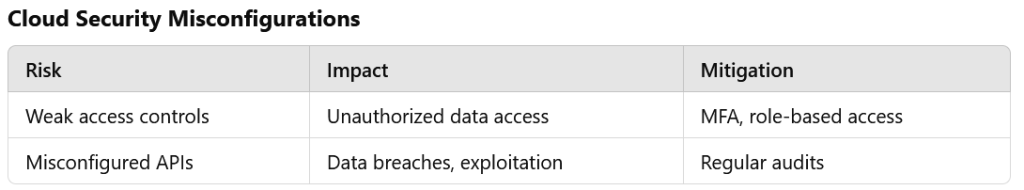
Cloud environments are often targeted by attackers seeking to exploit misconfigurations, weak access controls, or unencrypted data. Common vulnerabilities include improperly secured application programming interfaces (APIs) and overly permissive access permissions.
To counter these threats, organizations should regularly review and optimize their cloud configurations. Automating these reviews can ensure continuous compliance with security best practices.
Strong access controls are a cornerstone of cloud security. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access management limit who can access sensitive data and under what conditions.
Encryption is another critical defense, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption keys.
Data visibility and monitoring are essential components of cloud security. Organizations should use tools to track data flows and detect anomalies in real time, enabling quick responses to potential threats.
Additionally, frequent audits and security assessments help identify weaknesses and address them proactively.
The dynamic nature of cloud environments adds another layer of complexity. As businesses integrate new applications and services, the attack surface expands. Security measures must evolve alongside these changes, requiring organizations to adopt flexible and adaptive strategies.
By prioritizing cloud security, organizations can reap the full benefits of cloud computing without compromising the integrity of their data. A comprehensive approach to protecting cloud environments ensures that businesses remain resilient against threats, enabling them to thrive in the digital age.
Cloud Security Preparation Tips
- Understand Shared Responsibility: Recognize the security obligations of both the cloud provider and your organization.
- Implement Strong Access Controls: Ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive cloud data.
- Regularly Review Configurations: Continuously assess and adjust cloud settings to maintain optimal security.
5. Ransomware Readiness: Preparing for Potential Attacks
Ransomware has become one of the most prevalent and devastating cyber threats in recent years. Cybercriminals use this type of malware to encrypt an organization's data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid — often in cryptocurrency.
As these attacks grow in sophistication and scale, businesses and individuals alike face increased risks. Ransomware doesn't just affect large corporations; small businesses, government institutions, healthcare providers, and even private citizens are all potential targets.
Preparing for such incidents is essential to minimize damage and recover swiftly.
The first step in ransomware readiness is recognizing the common methods of attack. Phishing emails, malicious links, and unsecured remote desktop protocols (RDP) are often used to deliver ransomware. Organizations must educate their employees on how to recognize and avoid these threats.
Regular training programs and simulated phishing tests can help reinforce awareness and reduce human error, which is often the entry point for ransomware.
A robust incident response plan is another critical element of preparedness. This plan should outline the steps to take if a ransomware attack occurs, including isolating affected systems, communicating with stakeholders, and engaging with cybersecurity experts. Having a clear strategy in place ensures that responses are swift and coordinated, reducing downtime and potential losses.
Regular backups are a cornerstone of ransomware readiness. By maintaining up-to-date and secure backups of critical data, organizations can recover without paying the ransom. These backups should be stored in multiple locations, including offline or "air-gapped" storage, to prevent them from being compromised during an attack.
Testing the restoration process periodically ensures that backups can be relied upon when needed.
Additionally, deploying strong endpoint protection and implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) can significantly reduce the likelihood of ransomware infiltrating systems. Monitoring network activity for unusual patterns can also help detect ransomware attempts early, allowing organizations to intervene before significant damage occurs.
Ransomware attacks thrive on panic and unpreparedness. By taking proactive steps - educating employees, securing data, and establishing a solid response framework - organizations can limit the impact of an attack and recover quickly without succumbing to ransom demands.
This readiness not only protects data but also preserves trust and confidence among stakeholders.
Ransomware Readiness Preparation Tips
- Develop Incident Response Plans: Create and regularly update strategies to respond effectively to ransomware attacks.
- Conduct Regular Backups: Maintain up-to-date backups of critical data to facilitate recovery without paying ransoms.
- Educate Employees: Train staff to recognize phishing attempts and other common ransomware delivery methods.
6. Supply Chain Security: Ensuring Trust in Third-Party Partnerships
In today's interconnected world, businesses increasingly rely on third-party vendors and service providers to operate efficiently. While these partnerships offer numerous benefits, they also introduce vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
Supply chain attacks, where hackers infiltrate an organization by compromising one of its third-party vendors, have become a growing threat. These attacks allow malicious actors to bypass traditional security measures by targeting weaker links in the supply chain.
Securing these partnerships is essential to safeguard sensitive data, maintain operational integrity, and protect against indirect attacks.
One of the biggest challenges in supply chain security is the varying levels of cybersecurity maturity among vendors. Smaller vendors or suppliers may lack the resources or expertise to implement robust security measures, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Once attackers gain access to a vendor's systems, they can use that foothold to infiltrate the networks of larger, more secure organizations.
To address this risk, businesses must thoroughly vet their partners' cybersecurity practices before establishing a relationship.
Conducting regular risk assessments is crucial to understanding potential vulnerabilities in the supply chain. Organizations should evaluate vendors' security postures, policies, and incident response capabilities.
Establishing clear cybersecurity requirements in contracts and service-level agreements (SLAs) ensures that third parties adhere to a minimum standard of protection. These agreements should also include provisions for timely notification in case of a breach affecting the vendor.
Continuous monitoring of third-party access is another critical aspect of supply chain security. Businesses should track and restrict what systems and data vendors can access, ensuring that permissions align with their roles. Implementing technologies like network segmentation can limit the impact of a potential breach, preventing attackers from moving laterally within an organization's systems.
Additionally, fostering a culture of collaboration and transparency with vendors is essential. Sharing threat intelligence and providing guidance on best practices can help strengthen the overall security of the supply chain. Encouraging vendors to adopt measures such as multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and endpoint protection ensures that all parties contribute to a secure ecosystem.
In an era where supply chain attacks are becoming more sophisticated, businesses cannot afford to overlook this critical aspect of cybersecurity.
By proactively addressing third-party risks, organizations can protect themselves from cascading effects of a breach, maintain trust with stakeholders, and ensure the resilience of their operations.
Supply Chain Security Preparation Tips
- Assess Vendor Security Posture: Evaluate the cybersecurity measures of partners and suppliers.
- Establish Clear Security Requirements: Set and enforce security standards for all third-party collaborations.
- Monitor Third-Party Access: Keep track of the data and systems that external partners can access.
7. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Cybersecurity: Enhancing Defense Mechanisms
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the cybersecurity landscape, offering innovative solutions to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats more effectively. AI-powered systems excel at analyzing vast amounts of data in real time, identifying patterns, and detecting anomalies that could indicate malicious activity.
This ability to process and learn from data at unprecedented speeds gives organizations a significant advantage in their fight against cyber threats.
However, the same technology that bolsters defense mechanisms can also be weaponized by cybercriminals, creating a double-edged sword in the realm of cybersecurity.
On the defensive side, AI is particularly effective in areas like threat detection, where traditional methods may fall short. Machine learning algorithms can sift through massive datasets to identify unusual activities, such as unauthorized access attempts, abnormal data transfers, or suspicious network behavior.
These tools can also adapt over time, learning from new threats to become more precise in identifying potential risks. This capability allows organizations to respond to emerging threats proactively, often mitigating risks before they escalate into breaches.
AI also plays a critical role in automating responses to cyber incidents. For instance, AI-driven systems can isolate compromised accounts, block malicious traffic, or deploy patches to address vulnerabilities without requiring human intervention. This automation not only accelerates response times but also reduces the workload on cybersecurity teams, enabling them to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine tasks.
However, cybercriminals are also harnessing the power of AI to enhance their attacks. They use AI to create highly convincing phishing emails, develop malware that adapts to evade detection, and automate attacks on a massive scale. These advancements make it more challenging for traditional security measures to keep up, necessitating the adoption of equally sophisticated defense mechanisms.
To counter these threats, organizations must invest in AI-driven cybersecurity tools while staying informed about the ways attackers might exploit AI. Regularly updating systems, conducting AI-specific threat assessments, and fostering expertise in AI within cybersecurity teams are essential steps to maintain a strong defense.
Collaboration between AI developers, cybersecurity experts, and policymakers is also critical to ensure that advancements in AI are used ethically and responsibly.
As AI continues to shape the future of cybersecurity, its dual role as a tool for defense and a potential weapon for attackers underscores the importance of staying ahead in the technological arms race.
By leveraging AI responsibly and proactively, organizations can enhance their resilience against increasingly sophisticated threats while mitigating the risks posed by malicious actors.
AI Preparation Tip
- Adopt AI-Powered Security Tools: Utilize AI to analyze patterns and detect anomalies indicative of cyber threats.
- Stay Informed About AI Threats: Keep abreast of how malicious actors might use AI and develop countermeasures.
- Invest in AI Expertise: Build a team knowledgeable in AI to effectively implement and manage AI-driven security solutions.
8. Internet of Things (IoT) Security: Protecting Connected Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way we interact with technology, enabling devices from smart thermostats and home assistants to industrial sensors and medical equipment to communicate seamlessly over the internet. While this interconnectedness brings unparalleled convenience and efficiency, it also significantly expands the attack surface for cyber threats. Each connected device serves as a potential entry point for attackers, making IoT security a critical priority for individuals, businesses, and governments alike.
One of the primary challenges of IoT security is the sheer diversity and volume of devices. Many IoT devices lack robust built-in security features, often prioritizing cost, and usability over protection. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by hackers to gain unauthorized access to networks, steal sensitive data, or even disrupt critical infrastructure. For instance, a compromised smart home device could provide a gateway to the owner’s entire network, or a vulnerable industrial IoT sensor could lead to significant operational downtime.
Securing IoT devices begins with ensuring proper authentication and access controls. Devices should require strong, unique passwords and, where possible, support multi-factor authentication (MFA). Default credentials, which are often pre-configured and widely known, must be changed immediately after installation. Additionally, implementing network segmentation can isolate IoT devices from other parts of a network, minimizing the impact of a potential breach.
Regular updates and firmware patches are essential to address vulnerabilities as they are discovered. Regular updates and patches can reduce IoT vulnerabilities by 80%. Many IoT devices operate on outdated software, making them prime targets for attackers. Organizations and individuals must ensure that devices are updated promptly and that unsupported devices are replaced with newer, more secure models.
Monitoring and managing IoT networks are equally important. Tools that provide visibility into connected devices, their activities, and potential risks help detect and respond to unusual behavior early. For businesses, implementing security frameworks specific to IoT, such as those outlined by industry standards, ensures a consistent and proactive approach to safeguarding connected devices.
As IoT adoption continues to grow, ensuring the security of these devices is vital for maintaining overall network integrity and trust. While the benefits of IoT are transformative, they come with significant responsibilities to protect these devices from being exploited. By prioritizing IoT security, individuals and organizations can embrace the convenience of connected technology while minimizing the risks associated with it.
IoT Preparation Tips
- Implement Device Authentication: Ensure that only authorized devices can connect to your network.
- Regularly Update Firmware: Keep device software current to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Segment IoT Devices: Isolate IoT devices on separate network segments to contain potential breaches.
9. Data Privacy Regulations: Complying with Evolving Laws
In an age where personal data is increasingly valuable and vulnerable, governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter data privacy laws to protect individuals and hold organizations accountable for how they handle information.
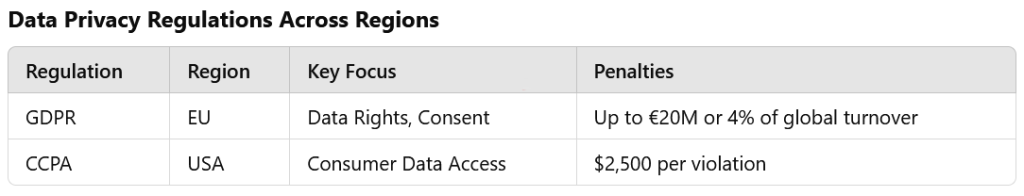
Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, and similar laws in other regions are designed to ensure that businesses prioritize transparency, security, and respect for individual rights when processing personal data.
These laws impose significant obligations on organizations, ranging from obtaining clear and informed consent before collecting data to ensuring robust security measures are in place to prevent breaches. They also grant individuals rights over their data, such as the ability to access, correct, or delete their information. For organizations, compliance is not just a legal necessity but also a trust-building exercise, as consumers are increasingly aware of and concerned about how their data is used.
One of the challenges businesses face is the dynamic nature of these regulations. Data laws continue to evolve, with new rules and amendments emerging in response to technological advancements and public demand for greater control over personal information. Organizations must stay updated on these changes to avoid non-compliance, which can result in substantial fines, legal actions, and reputational damage.
To stay up to date on security regulations, regularly monitor updates from official regulatory bodies, subscribe to industry newsletters, and attend relevant training and webinars.
Compliance requires a multi-faceted approach. Organizations must implement data minimization practices, collecting only the information necessary for their operations and ensuring it is used for lawful and transparent purposes. They must also maintain clear and accessible privacy policies, informing users about what data is collected, how it is used, and their rights regarding that data. Regular audits and impact assessments can help identify potential risks and ensure that data protection measures are effective.
Training employees on data privacy best practices is equally essential, as human error remains a common cause of data breaches. By fostering a culture of accountability and awareness, organizations can minimize risks and ensure compliance at every level.
Adhering to data privacy regulations is not only about avoiding penalties; it’s about demonstrating respect for individuals' rights and building trust with customers. As these laws become more stringent and widespread, proactive compliance will be a defining characteristic of responsible and successful businesses in the digital age.
Data Privacy Regulations Preparation Tips
- Stay Updated on Laws: Regularly monitor changes in local and global privacy regulations to ensure compliance.
- Data Minimization: Collect only the data you truly need and ensure it is processed for clear, lawful purposes.
- Invest in Privacy Training: Educate employees on data privacy best practices and legal obligations.
- Transparency Matters: Clearly inform users how their data is collected, stored, and used.
10. Humancentric Cybersecurity: Empowering the Individual
In the intricate world of cybersecurity, technology alone cannot guarantee safety. Despite advances in automated systems and sophisticated tools, the human factor often remains the weakest link in the security chain.
Cybercriminals frequently exploit human behaviors, capitalizing on mistakes such as clicking on phishing emails, downloading malicious attachments, or using easily guessable passwords. To counter these vulnerabilities, a human-centric approach to cybersecurity is essential - one that emphasizes awareness, education, and accountability at every level of an organization.
The first step in fostering human-centric cybersecurity is recognizing that most breaches begin with human error. Phishing campaigns, for instance, often target employees through legitimate emails designed to trick them into revealing sensitive information or granting unauthorized access.
To combat this, regular training sessions that educate employees on identifying and responding to such threats are crucial. Simulated phishing tests can further reinforce this training, helping individuals recognize suspicious activity without real-world consequences.
Strong password practices are another cornerstone of human-centric cybersecurity. Encouraging the use of complex, unique passwords and adopting password managers can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should also be implemented as an additional layer of defense, ensuring that even if a password is compromised, access to systems remains protected.
Creating a culture of accountability is equally important. This involves making cybersecurity everyone’s responsibility, not just that of the IT or security teams. Employees should feel empowered to report suspicious activities without fear of blame or retribution, as early detection is key to mitigating threats. Additionally, clear and accessible cybersecurity policies help individuals understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining a secure environment.
Leadership plays a vital role in shaping this culture. When executives and managers prioritize cybersecurity, it sets a tone for the entire organization, demonstrating its importance and encouraging adherence to best practices. Regular communication about threats, successes, and ongoing efforts further reinforces the collective responsibility for security.
Finally, human-centric cybersecurity is not just about preventing mistakes but also about empowering individuals to be proactive defenders of their digital environments. By equipping employees and individuals with the knowledge, tools, and support they need, organizations can turn the human factor from a liability into a critical asset in their cybersecurity strategy. This approach not only reduces risks but also fosters confidence and resilience in an increasingly interconnected world.
Humancentric Cybersecurity Preparation Tips
- Regular Training Programs: Conduct sessions on recognizing phishing attempts, securing personal devices, and understanding basic cybersecurity principles.
- Promote Strong Passwords: Encourage the use of complex passwords and password managers.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security by requiring multiple steps to verify identity.
- Empower Employees: Make cybersecurity resources accessible and provide support for individuals facing digital challenges.
Cybersecurity in 2025
Cybersecurity in 2025 is about staying ahead of ever-evolving threats through proactive measures and fostering a culture of awareness.
Key trends include:
- Continuous monitoring
- Securing critical systems like Active Directory
- Visualizing threats with attack graphs
- Safeguarding cloud and IoT environments
Other essential steps must address ransomware, ensure third-party security, and leverage AI for comprehensive protection. Compliance with data privacy regulations and empowering individuals through education round out a robust cybersecurity strategy
By focusing on these ten trends, individuals and organizations can navigate the digital world more safely and confidently. Cybersecurity isn't just a technical necessity — it's a shared responsibility that empowers everyone to thrive in an interconnected future.
ERMProtect’s Role in Your 2025 Cybersecurity Plan
ERMProtect is a leading provider of cybersecurity and risk management solutions, designed to help organizations strengthen their defenses against emerging threats. With expertise in various industries, ERMProtect offers comprehensive services that address the full spectrum of cybersecurity needs, from risk assessments and compliance audits to advanced threat detection and response.
Our proactive approach ensures that vulnerabilities are identified and addressed before they can be exploited, reducing the likelihood of breaches, and minimizing potential damage.
We excel in areas such as continuous threat monitoring, ransomware preparedness, and securing complex environments such as cloud platforms and IoT networks. In addition, we support organizations in complying with ever-changing data privacy regulations by providing tailored solutions that meet legal requirements while maintaining operational efficiency.
Our emphasis on employee training and education helps businesses tackle the human element of cybersecurity, empowering staff to recognize and prevent cyber threats effectively.
Whether an organization needs assistance in implementing advanced cybersecurity technologies or improving its existing framework, ERMProtect’s services are designed to enhance resilience and foster a culture of security.
By partnering with ERMProtect, businesses can focus on their growth and innovation with confidence, knowing their digital assets are well-protected.
About the Author
Dr. Rey Leclerc Sveinsson is an expert in Privacy and Data Protection, Information Security, and Technology Governance, Risk & Compliance (IT GRC). He has developed information assurance programs for major organizations globally during his career as well as serving as a Consultant for ERMProtect. He has a PhD in Information Systems and multiple master’s degrees in the areas of privacy, information technology, and cybersecurity laws.
Subscribe to Our Weekly Newsletter

Turn your employees into a human firewall with our innovative Security Awareness Training.
Our e-learning modules take the boring out of security training.
Intelligence and Insights

Quantum Computing Puts Today’s Encryption at Risk

Are You Prepared for an AI-Powered Cyber Attack?