The Most Common Problems with PCI DSS Certification Implementation
By Rey LeClerc Sveinsson, PhD
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a global framework designed to ensure the security of cardholder data. While businesses aim to comply with these strict standards, there are several hurdles during the implementation process that can hinder progress.
Below are the most common problems organizations face with PCI DSS certification implementation and the solutions to overcome them.
1. Incomplete Scope Definition
Incomplete scope definition is a common challenge in PCI DSS certification implementation, often resulting from the failure to identify and include all systems that store, process, or transmit cardholder data (CHD).
This oversight can lead to:
- Security gaps
- Increased risk of breaches
- Non-compliance penalties
The cardholder data environment (CDE) extends beyond primary systems to include any connected systems that could impact its security, making accurate scoping essential.
Key causes of incomplete scoping include a lack of understanding of interconnected systems, dynamic IT environments, overlooked third-party dependencies, and assumptions about low-risk systems.
Overcoming Incomplete Scope Definition Challenges
To address this, organizations should conduct regular scoping assessments, maintain an updated inventory of all relevant systems, and include third-party vendors in compliance evaluations. Tools such as network discovery software and asset management platforms can help identify connected systems.
Proper documentation of scoping decisions, employee training, and collaboration with Qualified Security Assessors (QSAs) further support effective scoping. By prioritizing accurate scope definition and leveraging practices such as network segmentation and penetration testing, businesses can enhance security, reduce compliance costs, and ensure comprehensive PCI DSS certification coverage.
2. Weak Access Control
Insufficient access control over sensitive cardholder data is a significant vulnerability that can lead to unauthorized access, potentially exposing the data to misuse, theft, or breaches.
Poor access control often arises from:
- A lack of stringent policies
- Outdated systems
- Failure to limit access based on roles and responsibilities.
For example, granting excessive permissions to employees or not revoking access for former staff increases the likelihood of accidental or malicious misuse of sensitive data.
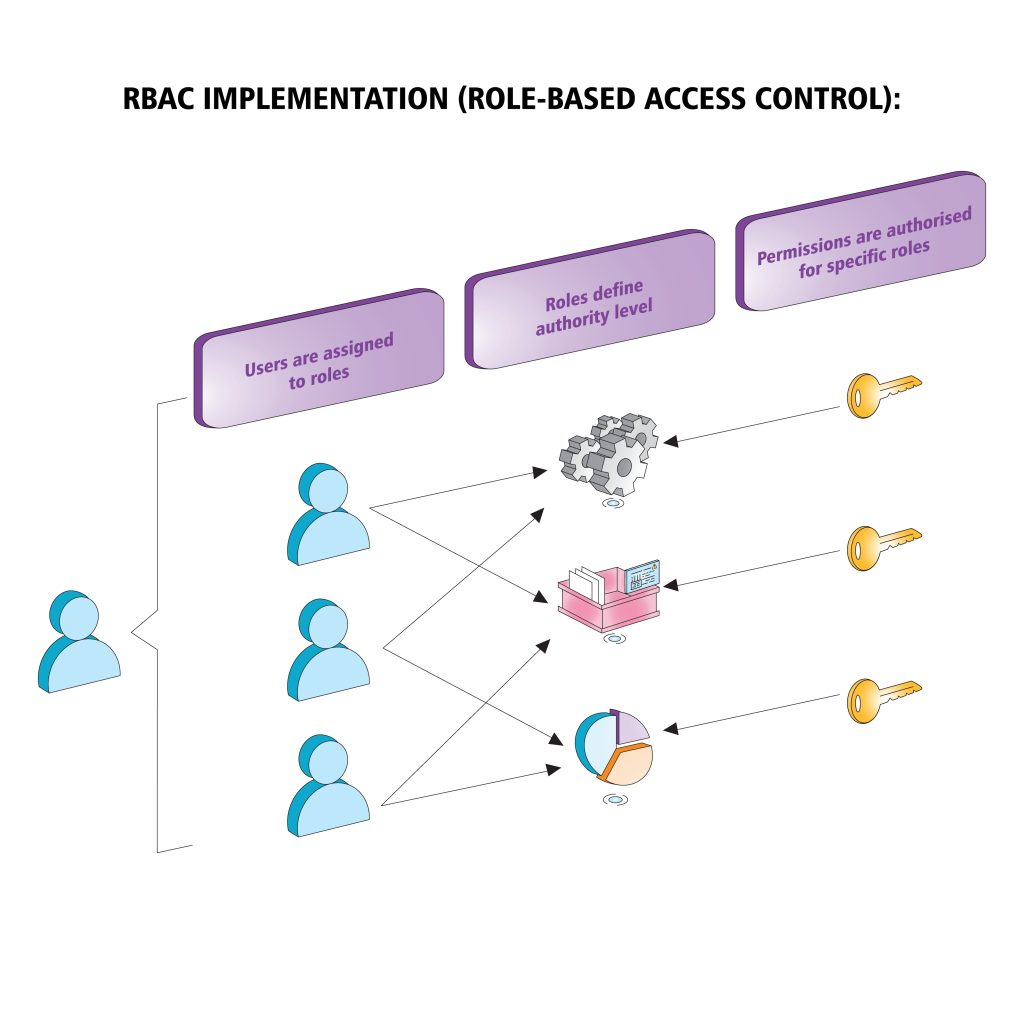
To mitigate this risk, organizations should implement role-based access controls (RBAC), which restrict access to cardholder data based on an individual’s specific job role and operational need-to-know. This ensures that employees can only access the information necessary for their responsibilities, minimizing the attack surface.
Improving Access Control
Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) and regularly audit user privileges to ensure only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information. Regular audits of user privileges are essential to identify and remediate over-provisioning of access rights.
These audits help organizations uncover and address discrepancies, such as unauthorized access or roles that no longer align with an individual’s job requirements.
Additionally, enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security, reducing the risk of unauthorized access even if credentials are compromised.
By combining RBAC, periodic audits, and advanced authentication measures, businesses can significantly enhance the security of cardholder data, ensuring compliance with PCI DSS certification requirements while safeguarding their operations against access-related vulnerabilities.
3. Poor Encryption Practices
Transmitting data over open networks without proper encryption poses a significant security risk, as it leaves sensitive cardholder data vulnerable to interception and breaches.
The absence of encryption or reliance on outdated, weak encryption protocols increases the likelihood of data being compromised during transmission.
Strengthening Encryption Practices
To mitigate this risk, organizations must adopt strong encryption protocols, such as TLS 1.2 or higher, to secure data as it moves across networks. Additionally, encrypting data stored at rest provides an added layer of protection, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure even if storage systems are breached.
Implementing these robust encryption practices is essential for maintaining compliance with PCI DSS and safeguarding cardholder data from potential threats.
4. Inconsistent Patch Management
Inconsistent patch management is a common issue that creates exploitable vulnerabilities, leaving systems open to potential attacks.
Delays in applying security patches or inconsistencies in the patching process can result from a lack of automation, resource constraints, or oversight, giving attackers opportunities to exploit known weaknesses.
Advancing Patch Management
Organizations should automate patch management processes to ensure timely updates across all systems. Regular vulnerability scans should also be conducted to identify and remediate any gaps in patching, providing an added layer of assurance that systems remain secure and up to date.
These proactive measures are essential for reducing risks, maintaining compliance, and protecting sensitive data from evolving threats.
5. Inadequate Logging and Monitoring
Inadequate logging and monitoring of systems can significantly hinder an organization’s ability to detect suspicious activities in a timely manner, increasing the likelihood of data breaches.
Without comprehensive logs or active monitoring, unauthorized access or security threats can go unnoticed, allowing potential attackers to exploit vulnerabilities.
Boosting Logging and Monitoring Efforts
Organizations should implement centralized logging systems that consolidate logs from all critical components into a single platform for streamlined analysis.
Real-time monitoring tools should also be deployed to detect and respond to unauthorized access or potential threats promptly.
These monitoring measures:
- Enhance visibility
- Improve incident response capabilities
- Reduce the risk of data breaches
Resulting in better protection for sensitive information and compliance with security standards.
6. Non-Compliant Third-Party Vendors
Non-compliant third-party vendors pose a significant risk to organizations. This occurs by potentially exposing cardholder data to vulnerabilities if they fail to adhere to PCI DSS certification standards.
Vendors often play a critical role in processing, storing, or transmitting sensitive information, and any lapses in their compliance can jeopardize the security of the entire payment ecosystem.
Forcing Third-Party Vendors To Comply
Organizations must enforce strict vendor compliance policies that mandate adherence to PCI DSS requirements.
Regular audits should be conducted to:
- Assess third-party vendors’ compliance status
- Identify potential weaknesses
- Ensure they meet the necessary security standards
By maintaining strong oversight of third-party vendors, organizations can safeguard cardholder data and uphold the integrity of their compliance efforts.
7. Lack of Security Awareness Training
A lack of security awareness training among employees can lead to inadvertent mishandling of sensitive cardholder data, increasing the risk of compliance violations and security breaches.
Employees who are unaware of PCI DSS certification requirements may unintentionally engage in risky behaviors or fail to recognize potential threats, such as phishing attempts or improper data handling practices.
Beefing Up Security Awareness Training
Organizations should implement ongoing security awareness training programs. These programs should educate employees on the importance of data protection, highlight key PCI DSS requirements, and provide practical guidance on recognizing and mitigating security threats.
Regular training reinforces a culture of security, empowering employees to play an active role in safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
8. Insufficient Data Retention Policies
Insufficient data retention policies can significantly increase the risk of a data breach by prolonging the storage of sensitive cardholder information beyond what is necessary.
Retaining data unnecessarily not only expands the potential attack surface but also exposes the organization to non-compliance with PCI DSS standards and other regulatory frameworks.
Improving Data Retention Policies
Organizations should implement and enforce strict data retention and deletion policies. Data should be stored only for as long as it is required for legitimate business purposes, after which it should be securely deleted.
By minimizing the unnecessary retention of sensitive information, organizations can reduce their exposure to potential breaches and strengthen their overall data protection posture.
9. Lack of Network Segmentation
A lack of network segmentation can significantly increase the risk of unauthorized access to systems storing cardholder data, making them more vulnerable to attacks.
When networks are not properly segmented, the cardholder data environment (CDE) becomes exposed to potential threats from other parts of the network, including systems with lower security standards.
Establishing Network Segmentation
Organizations should implement effective network segmentation strategies to isolate the CDE from non-sensitive systems.
By creating clear boundaries and limiting access between segmented networks, businesses can reduce the risk of data exposure, improve overall security, and simplify compliance with PCI DSS requirements.
10. Insecure Remote Access
Insecure remote access to the cardholder data environment (CDE) can create significant security vulnerabilities, providing potential entry points for unauthorized individuals.
Without strong security controls in place, remote access channels become a weak link, exposing sensitive data to breaches and non-compliance risks.
Securing Remote Access
Organizations should enforce the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security for remote access. Additionally, implementing secure VPN solutions ensures encrypted connections, safeguarding data transmissions over public or untrusted networks.
By combining MFA and secure VPN usage, businesses can effectively protect remote access channels and maintain the integrity of their CDE.
A Review of PCI DSS Certification Compliance Requirements
Achieving PCI DSS compliance requires addressing these common issues. Businesses must regularly review systems, enforce strong access control measures, use encryption protocols, automate patch management, and conduct regular vulnerability scans to protect cardholder data.
Additionally, monitoring logs, educating employees, and ensuring vendor compliance play crucial roles in maintaining robust data security.
Tips for Successful PCI DSS Certification Implementation
- Regularly Assess Scope: Continuously evaluate which systems fall within the PCI DSS scope.
- Enhance Vendor Oversight: Implement third-party risk management programs.
- Automate and Monitor: Utilize automated tools for patch management, logging, and vulnerability scanning.
- Educate Your Team: Invest in employee training programs to ensure awareness of PCI DSS compliance.
- Adopt Strong Encryption and Key Management: Use modern encryption protocols and maintain rigorous key management practices.
By addressing these challenges, businesses can ensure compliance with PCI DSS, protect customer data, and strengthen their overall security posture. For more detailed guidance, consult with cybersecurity professionals or PCI DSS certification experts.
PCI DSS Certification with ERMProtect
ERMProtect can play a pivotal role in enhancing an organization's compliance with PCI DSS and fortifying its overall cybersecurity posture. As a leading provider of risk management and security solutions, ERMProtect offers a comprehensive suite of services designed to address the challenges of implementing and maintaining PCI DSS certification compliance. Our expertise includes conducting detailed risk assessments, performing vulnerability scans, and providing penetration testing to identify and mitigate security weaknesses.
ERMProtect also supports businesses with network segmentation strategies, secure system configurations, and encryption protocols to protect cardholder data. Additionally, we offer robust training programs to raise security awareness among employees and ensure adherence to best practices.
By partnering with ERMProtect, organizations can streamline PCI DSS certification compliance efforts, safeguard sensitive data, and build a resilient defense against evolving cyber threats.
For more information about ERMProtect PCI DSS certification services, please contact Judy Miller at [email protected] or call 305-447-6750.
About the Author
Dr. Rey Leclerc Sveinsson is an expert in Privacy and Data Protection, Information Security, and Technology Governance, Risk & Compliance (IT GRC). He has developed information assurance programs for major organizations globally during his career as well as serving as a Consultant for ERMProtect. He has a PhD in Information Systems and multiple master’s degrees in the areas of privacy, information technology, and cybersecurity laws.
Intelligence and Insights

Cybersecurity Blind Spot: Why Physical Security Is Now the Easiest Way In

Red, Blue, & Purple Teaming: Unified Strategy Organizations Can’t Ignore