Guide to Penetration Testing and Advanced Techniques in Penetration Testing Services
By Esteban Farao, ERMProtect Director of IT Consulting
(Editor’s Note: Esteban Farao has been an ethical hacker performing penetration testing for more than 20 years. He’s broken into the information systems of banks and other highly sensitive organizations in 40+ industry verticals. Here is his comprehensive guide to basic and advanced techniques.)
Penetration testing plays a crucial role in enhancing the security posture of an organization because ethical hackers (like me) can identify deficiencies before somebody malicious can exploit them.
There are several formal definitions of penetration testing within the cybersecurity industry including these:
- According to the NIST (NIST SP800-12 Rev. 1, NIST SP800-53 Rev. 5, NIST SP800-53A Rev. 5), penetration testing is a test methodology in which assessors, typically working under specific constraints, attempt to circumvent or defeat the security features of a system.
- According to the NCSC-UK, penetration testing is a method for gaining assurance in the security of an IT system by attempting to breach some or all of that system's security, using the same tools and techniques as an adversary might.
Simply put, penetration testing uncovers vulnerabilities in people, technology, and processes. A key distinction of this assessment compared to others, such as audits or configuration assessments, is the interactive nature of the control evaluation. Unlike static assessments, penetration testing involves dynamic interaction with the system.
Roles of Penetration Testing Services
Here are some primary roles for this type of assessment:
- Identifying Security Weaknesses - The assessment helps organizations to identify vulnerabilities in their systems, networks, applications, and processes. By simulating real-world attack scenarios, penetration testers can uncover weaknesses that could potentially be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access or compromise sensitive information.
- Assessing Defense Effectiveness – The assessment evaluates the effectiveness of an organization's security controls and defensive measures. By attempting to bypass security mechanisms such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls, penetration testers can assess whether these controls are properly configured and capable of resisting sophisticated attacks.
- Validating Compliance Requirements – The assessment helps organizations to validate compliance with industry regulations, standards, and best practices, such as PCI DSS, NIST, ISO 27001. By conducting regular tests and assessments, organizations can demonstrate due diligence in safeguarding sensitive data and meeting regulatory requirements.
- Improving Incident Response Preparedness - What better way to see if our organization is ready to respond to an attack than by simulating one? Using penetration testing, you can assess your incident response capabilities and readiness to detect, respond to, and mitigate security incidents. Once the gaps are identified, you can enhance your processes, technologies and incident response plan.
- Continuous Improvement - Penetration testing is an iterative process that fosters continuous enhancement of an organization's security posture. Through regular assessments and remediation of vulnerabilities, organizations can adapt to emerging threats, reinforce their defenses, and stay ahead of cyber adversaries.
Compliance Requirements in Penetration Testing Services
Today, the implementation of penetration testing is frequently referenced, either directly or indirectly, in various regulations, standards, and security best practices. It is an essential assessment that no organization should overlook.
- ISO/IEC 27001, which is the international standard for information security management systems (ISMS). The standard mentions penetration testing in several clauses (Clause 6: Planning and Clause 8: Operation) and also has a specific section in Annex A. For those who do not know what Annex A is, it is an inventory of security controls that were defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO.) To be more specific, the control A.12.6.1 (Technical Vulnerability Management) defined in Annex A includes penetration testing as one of the methods for identifying technical vulnerabilities in systems and applications. There is also a specific section (A.14.2.8) titled "Penetration Testing" that addresses the need for organizations to conduct penetration testing to assess the security of their information systems and environments.
As you can see, penetration testing services are a fundamental component of ISO/IEC 27001's approach to identifying and managing information security risks.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): PCI DSS is a set of security standards designed to ensure that all companies that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment. Penetration testing is a requirement under PCI DSS (Requirement 11.3) to assess the security of cardholder data environments. An organization must perform different types of penetration testing assessments annually and after a significant change in the IT environment.
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework: While it is not a regulation per se, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides guidance for organizations to manage and reduce cybersecurity risks. Penetration testing is often recommended as part of the "Identify," "Protect," and "Respond" functions outlined in the framework.
- New York State Department of Financial Services (NYDFS) Cybersecurity Regulation: This regulation requires financial services companies regulated by them to implement a cybersecurity program that includes penetration testing to assess the effectiveness of the security controls.
- Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA): FISMA requires federal agencies to develop, document, and implement an information security program to protect their information and information systems, including conducting regular security assessments such as penetration testing.
- Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS): D-FARS mandates specific security requirements for contractors and subcontractors doing business with the Department of Defense (DoD). It includes requirements for conducting penetration testing to protect controlled unclassified information (CUI).
- SOC2 Compliance: A SOC 2 examination is a report on controls at a service organization relevant to data security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, or privacy. Trust services Common Criteria CC4.1 talks about the performance of ongoing and separate evaluations such as penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and third-party assessments.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA mandates security standards to protect sensitive patient health information. While penetration testing is not explicitly mentioned in HIPAA regulations, it is often considered necessary to ensure the security of electronic protected health information (ePHI) and to comply with the Security Rule.
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA): Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), a law that protects the privacy of consumer information, requires for compliance the performance of annual penetration testing and regular vulnerability scanning.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): While CCPA does not explicitly mention penetration testing, it requires businesses to implement and maintain reasonable security procedures and practices appropriate to the nature of the personal information they collect. Penetration testing assessments can be considered part of these security measures.
How to Identify What Penetration Testing Services Are Needed
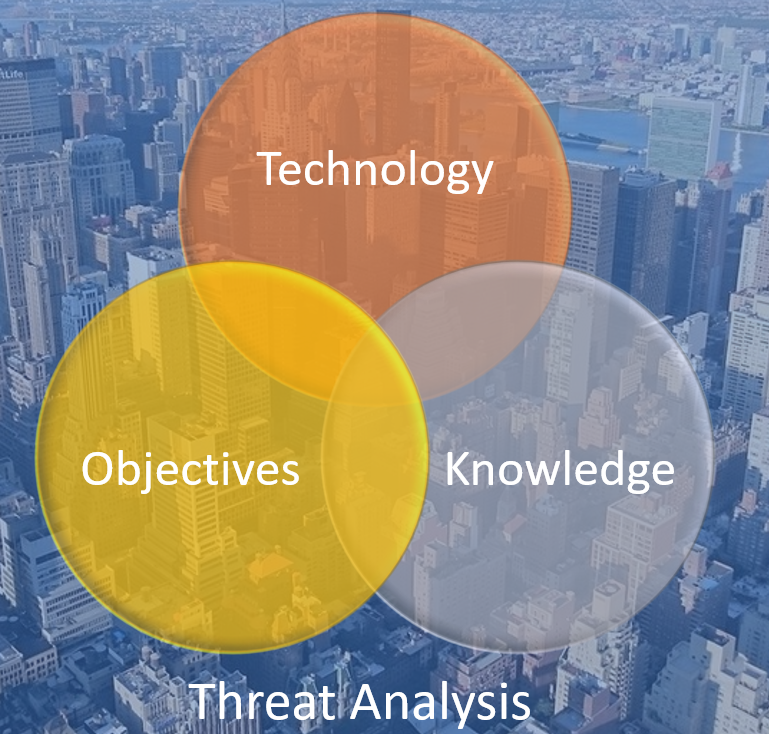
Without taking into consideration what regulation, standard or certification your organization must comply with, if you need to decide what penetration testing assessment your organization needs, you will need to perform a Threat Analysis. This means you must identify the potential threats facing the organization, assess the associated risks, and evaluate where vulnerabilities are most likely to exist or which threats are most probable to occur.
Based on this analysis, you can then determine the objective of the penetration test, the technology that is going to be involved, and the knowledge that the pen tester will be given prior to the assessment.
For instance, if you are implementing a new website with a payment solution, you may choose to conduct penetration testing on the application itself to ensure there are no vulnerabilities. You may also decide whether or not to give the pen tester the credentials during the tests. As part of your analysis, you might also consider performing network penetration testing on the environment where the website is hosted. If the website is hosted by a third-party provider, you may want to assess how the provider responds in the event of an attack on the site.
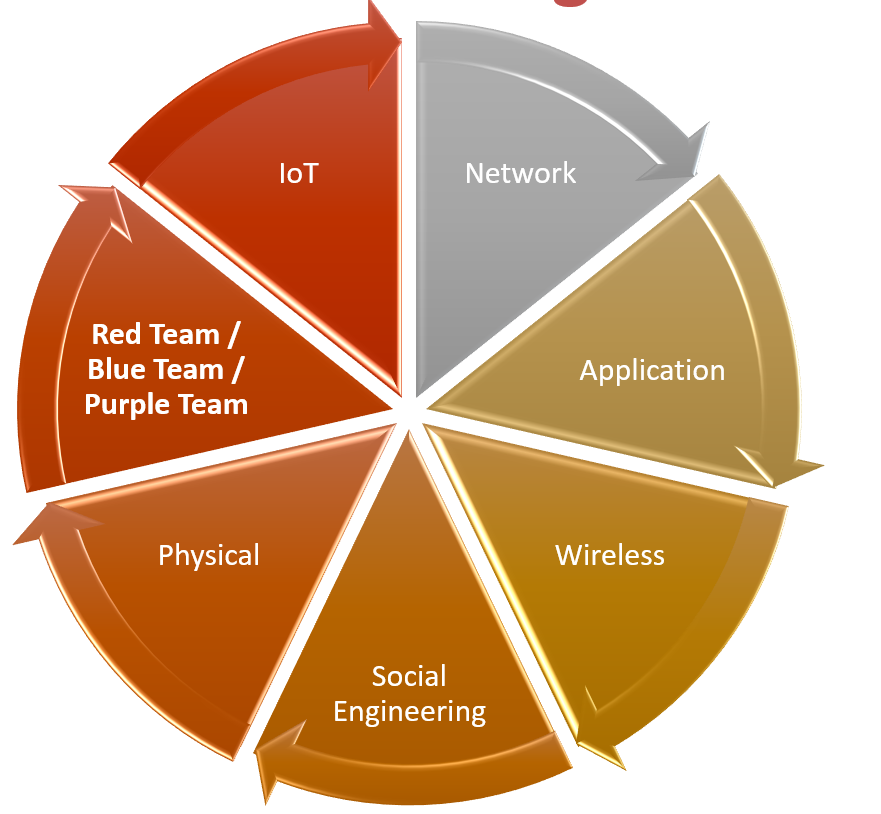
Types of Penetration Testing Services
The following graph illustrates several types of penetration testing assessments. The distinctions between them lie in the technology being evaluated and the specific objectives of the test. For example, if the focus is on people and processes, a social engineering test may be conducted. If the goal is to identify vulnerabilities more broadly, application penetration testing or network penetration testing can be performed.
Following is a concise explanation of each of the categories:
- Network Penetration Testing – This is what I call the classic or traditional penetration testing where it can be done from inside the organization internal network (Internal Network Penetration Testing) or from outside the organization network (External Network Penetration Testing). In the first case, we are emulating an internal threat actor and in the second case we are emulating an external threat actor. Most regulations that call for penetration testing are referring to internal and external network penetration tests.
- Application Penetration Testing – These assessments are only targeting the application itself regardless of where it was implemented. For example, if the application is a website, this test does not cover infrastructure, firewalls, IDS/IPS, and web server/service – only the application itself.
Keep in mind that this category includes several types of applications: web applications, mobile applications, and thick client applications.
- Wireless Penetration Testing - The most common assessment is the WiFi penetration testing which assesses the wireless access point of the organizations. However, under this category we can also evaluate Bluetooth, RFID, NFC, Zigbee, and Z-Wave.
- Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology that allows devices to communicate and exchange data. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a wireless communication technology that is an extension of Bluetooth technology. BLE is commonly used for wearable devices, IoT applications, and proximity sensing. BLE operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz and has a range of up to one hundred meters.
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) forms the foundation for NFC - RFID and uses radio waves to transmit data between objects and a reader. For example, a security tag on clothing at a store uses RFID.
- Near Field Communication(NFC) – Phones send small bits of data short distances without pairing like with Bluetooth NFC can act as an electronic identify document or keycard (such as Google Pay, Apple Pay.)
- Zigbee features low power consumption and low data rate, and is widely used in IoT and various embedded applications, such as home automation, wireless sensor networks, smoke and intruder warnings, building automation, etc.
- Z-Wave is a wireless communication protocol used primarily in smart home networks, allowing smart devices to connect and exchange control commands and data with each other
- IoT Penetration testing combines application, wireless, and network penetration testing. This applies to any device equipped with sensors that collect and exchange data. These devices must connect to a network and communicate with each other. In addition to the tests conducted in application, wireless, and network penetration assessments, this evaluation also includes analyzing the device's firmware for potential vulnerabilities, as these devices typically run on a minimal version of an operating system.
- Social Engineering assessments try to manipulate, influence, or deceive individuals to gain access to a computer system or obtain sensitive information. These tests help organizations assess their employees' knowledge of information security and their security practices. Various attack methods are used, including phishing, pretexting, baiting, tailgating, piggybacking, dumpster diving, and shoulder surfing.
- Physical Penetration Testing uses tools and techniques to bypass physical and technical security measures while minimizing damage to the organization. The primary goal is to demonstrate how an adversary could infiltrate the organization virtually undetected. Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) actors often employ tactics such as social engineering, covert entry, and tailgating (following an authorized person into a secure area) to circumvent security controls and gain access to restricted areas. These targeted attacks are designed to remain unnoticed for extended periods, posing a significant security risk.
There are several approaches to pen testing, as detailed below.
Classic Penetration Testing Services vs Red Teaming
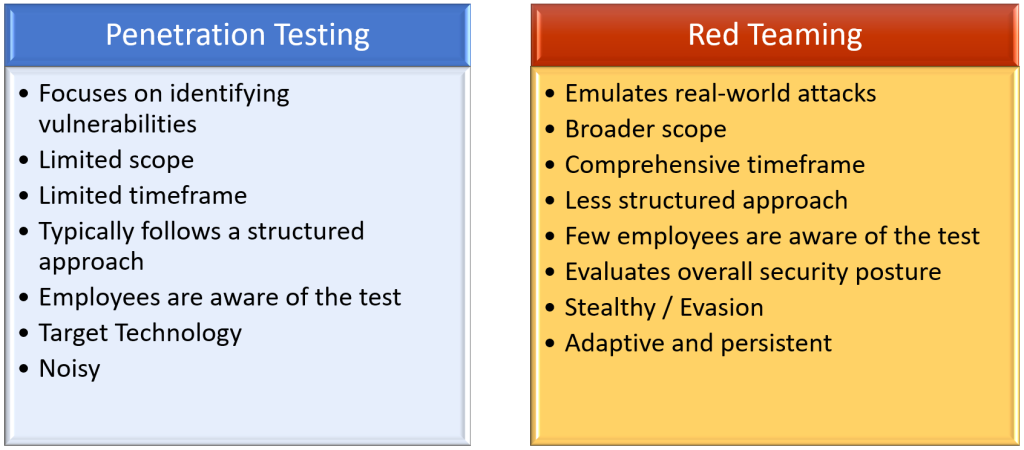
The most effective way to understand red teaming is by comparing it to traditional penetration testing assessments. This comparison highlights the distinct approaches and objectives of each, offering a clearer perspective on how red teaming goes beyond conventional penetration testing.
Classic Penetration Testing Services
These are the main characteristics of classic penetration testing engagement:
- Focuses on identifying vulnerabilities: Its primary aims are to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in a system, network, or application.
- Limited scope: Usually conducted within a defined scope, which could be specific systems, applications, or network segments.
- Limited timeframe: These engagements are usually very short in time since everybody is aware of the assessment.
- Typically follows a structured approach: The penetration testing often follows established methodologies such as OWASP, NIST, OSSTMM (Open-Source Security Testing Methodology Manual), CREST (Council of Registered Ethical Security Testers) SANS Penetration Testing Methodology, NIST SP 800-115.
- Employees are aware of the test: Since the main goal is to identify vulnerabilities, there is no need to conceal the test from the organization's employees.
- Target Technology: The assessment focuses on specific systems, devices, applications, and infrastructure components.
- Noisy: The assessment is not conducted stealthily, meaning the pentester will generate significant traffic while evaluating as many target technologies as possible within a predefined timeframe.
Red Teaming
These are the main characteristics of a red teaming engagement:
- Emulates real-world attacks: Red teaming simulates sophisticated, targeted attacks to assess an organization's readiness and response capabilities. For example, you can try to emulate the threat group APT28, the group that attempted to interfere with the U.S. presidential election back in 2016.
- Broader scope: Red team exercises typically have a broader scope, including a combination of several types of penetration testing categories such as physical security, social engineering, and human factors, in addition to technical aspects.
- Comprehensive timeframe: Since the goal is to replicate a real-world scenario, the assessment will take significantly more time. Additionally, it must remain as undetected as possible, with only a limited number of people within the organization aware that it is taking place.
- Less structured approach: Red team exercises may have less rigid methodologies compared to classic penetration testing allowing for greater flexibility and creativity.
- Few employees are aware of the test: To accurately simulate a real-world scenario, the assessment's execution is not disclosed to everyone. Only the employees responsible for approving the assessment will be informed.
- Evaluates overall security posture: This assessment goes beyond evaluating technical defenses; it also examines organizational processes, incident response capabilities, and human factors. By assessing these aspects, the evaluation provides a comprehensive understanding of an organization's overall security posture, finding potential weaknesses in both technology and human-driven security measures.
- Stealthy / Evasion: Unlike traditional penetration testing assessments, this evaluation must remain undetected to accurately simulate a real-world attack scenario.
- Adaptive and persistent: Red teams use advanced tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to emulate realistic threat actors, including persistence and lateral movement. For more detailed information, you can go to MITRE ATT&CK website https://attack.mitre.org/
Red Team – Blue Team – Purple Team
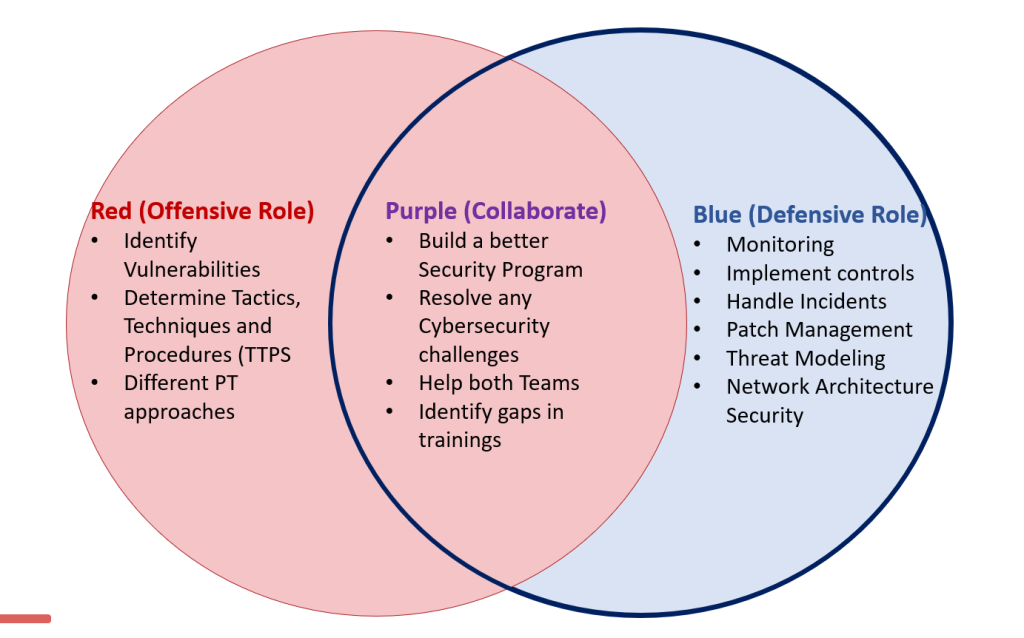
The following diagram depicts the characteristics of the Red, Purple, and Blue teams:
Red Team Role
In typical exercises, the red team assumes the offensive role. Initially, it conducts reconnaissance to find vulnerabilities and potential risks, then strategizes its methods of attack based on the weaknesses discovered. Throughout the exercise, the red team employs a range of tactics, including but not limited to:
• Performing penetration testing to find specific weaknesses
• Launching phishing, social engineering and other credential theft attacks
• Doing port scans
• Running vulnerability scans
Once the red team finds an opportunity, it selects the most effective tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to exploit it. This may involve infiltrating systems or breaching physical perimeters while working to evade detection by the blue team. These exercises serve as a valuable measure of the blue team’s defensive capabilities and their effectiveness in identifying and responding to threats.
Blue Team Role
As the counterpart to the red team, the blue team handles defense. Its role is to detect, confront, and mitigate the attacker’s efforts (red team). The blue team continuously monitors both current and emerging threats, while preparing to implement robust defenses to safeguard its systems. The objectives and tasks of the blue team include:
• Finding suspicious traffic patterns on networks, systems, and devices
• Searching for vulnerable areas and quickly responding to compromises
• Identifying red team attacks and blocking access
• Conducting internal and/or external vulnerability scans
• Collecting network traffic and forensic data to perform analysis and testing
• Understanding incident phases and how to respond appropriately
Purple Team Role
A purple team is grounded in a collaborative approach, designed to provide both red and blue teams with insights into both offensive and defensive strategies. The purple team methodology is business-oriented and milestone-focused, enabling both teams to use their strengths in addressing cybersecurity challenges. With a results-driven approach, purple teams:
• Identify gaps in training
• Test any previously untested TTPs
• Help teams acquire new security skills in real time
• Improve threat detection and response times
• Prioritize new risks to help minimize them earlier
• Provide recommendations to improve current security posture
• Analyze results and oversee remediation solutions
• Build a better security program
AI and Penetration Testing Services
Now, we are at the point where companies have diverse kinds of technologies and hundreds of thousands of IP addresses, making it more difficult for pen testers to check everything in a reasonable time with exact results.
This is why the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) has started to help pen testers overcome these obstacles.
Penetration Testing processes using AI and Machine learning enhance efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness. AI-powered penetration testing tools and techniques can automate certain aspects of the testing process, augment human analysts' capabilities, and provide deeper insights into security vulnerabilities. Here's how AI is utilized in penetration testing:
- Automated Vulnerability Discovery: AI algorithms can automatically scan networks, applications, and systems to identify potential vulnerabilities. These algorithms analyze large volumes of data to detect patterns indicative of security weaknesses, such as misconfigurations, outdated software, or known vulnerabilities.
- Dynamic Attack Simulation: AI-powered penetration testing tools can simulate sophisticated attack scenarios, including advanced persistent threats (APTs) and zero-day exploits, to assess an organization's defenses against real-world threats. These simulations help identify gaps in security controls and validate the effectiveness of defensive measures.
- Adaptive Testing Strategies: AI algorithms can adapt penetration testing strategies based on evolving threat landscapes, changes in the organization's infrastructure, or new attack vectors. By continuously learning from past experiences and incorporating current information, AI-driven testing approaches remain agile and responsive to emerging security challenges.
- Reduced False Positives: Machine Learning algorithms can help reduce the number of false positives generated during penetration testing. By applying advanced analytics and pattern recognition techniques, ML models can distinguish between genuine security threats and benign anomalies, thereby improving the accuracy of vulnerability assessments.
- Data Manipulation and Misinformation: AI algorithms can be used to generate realistic-looking fake images, videos, or text content. Malicious actors can use this technology to create convincing fake news articles, social media posts, or audio/video recordings to spread misinformation, manipulate public opinion, or discredit individuals or organizations.
Wrapping Up Penetration Testing Services
In conclusion, penetration testing assessments are crucial for strengthening an organization's security posture, as they provide valuable insights and help to:
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Penetration testing uncovers weaknesses in systems, networks, and applications that could be exploited by attackers.
- Validate Security Controls: Penetration testing validates the effectiveness of existing security measures.
- Improve Incident Response: Penetration testing provides insights into how systems and personnel respond to security incidents, enabling organizations to refine their incident response plans and procedures.
- Build Trust: Demonstrating a commitment to security through regular penetration testing can enhance trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders, bolstering reputation and credibility.
- Control Costs: Investing in penetration testing can ultimately save organizations money by preventing costly data breaches, downtime, and damage to reputation and brand image.
- Meet Compliance: This type of assessment is required in one way, or another, by regulations, standards, or best practices.
Penetration Testing Services with ERMProtect
At ERMProtect, our penetration testing services are unmatched. We have been conducting them for nearly three decades and take pride in our expertise, experience, and commitment to safeguarding our clients’ cybersecurity posture. For more information, please email Judy Miller at [email protected] or call 305-447-6750.
Subscribe to Our Weekly Newsletter
Intelligence and Insights

Are You Prepared for an AI-Powered Cyber Attack?

AI Privacy Risks